Search Results
We found 101 results for University of Arkansas in video, leadership, management, webinar, news & Other
video (82)
Inferior Oblique Myectomy
videoInferior oblique myectomy is a type of strabismus surgical procedure that aims to weaken an extraocular muscle by transecting it. The patient is a four old with a history of inferior oblique overaction and vertical strabismus, which can be corrected by resection of the inferior oblique muscle. The ointment was applied to the cornea. Forced ductions were performed and identified restriction of the inferior oblique. A conjunctival incision is made in the fornix. Tenon's capsule is dissected to expose the Inferior Oblique. The inferior oblique muscle is isolated using a Stevens tenotomy hook followed by Jameson muscle hooks. The inferior rectus was identified on a steven’s hook medially to the inferior oblique. The lateral rectus was then identified on a steven’s hook laterally to the inferior oblique. This was done to ensure that neither muscle was incorporated with the portions of the inferior oblique muscle to be cut. Wescott scissors were used to cut both ends of the muscle. Bipolar cautery forceps were used to cauterize the resected proximal and distal ends of the inferior oblique muscle. The two ends were released and the remaining muscle ends were allowed to retract into the orbit. The conjunctiva was closed using a plain gut suture. No complications arose during the procedure. Postoperatively, the patient had a subconjunctival hemorrhage, injection, and pain that decreased over the following week. Neomycin-polymyxin-dexamethasone drops were applied daily to prevent infection and inflammation. At the one follow-up, the redness and pain had resolved. Inferior oblique myectomy effectively treats inferior oblique overaction and vertical strabismus associated with this condition.
Phacoemulsification and IOL Implantation in an Iris Coloboma Case
videoWe present a case of cataract extraction and intraocular lens implantation in an eye with a congenital iris coloboma.
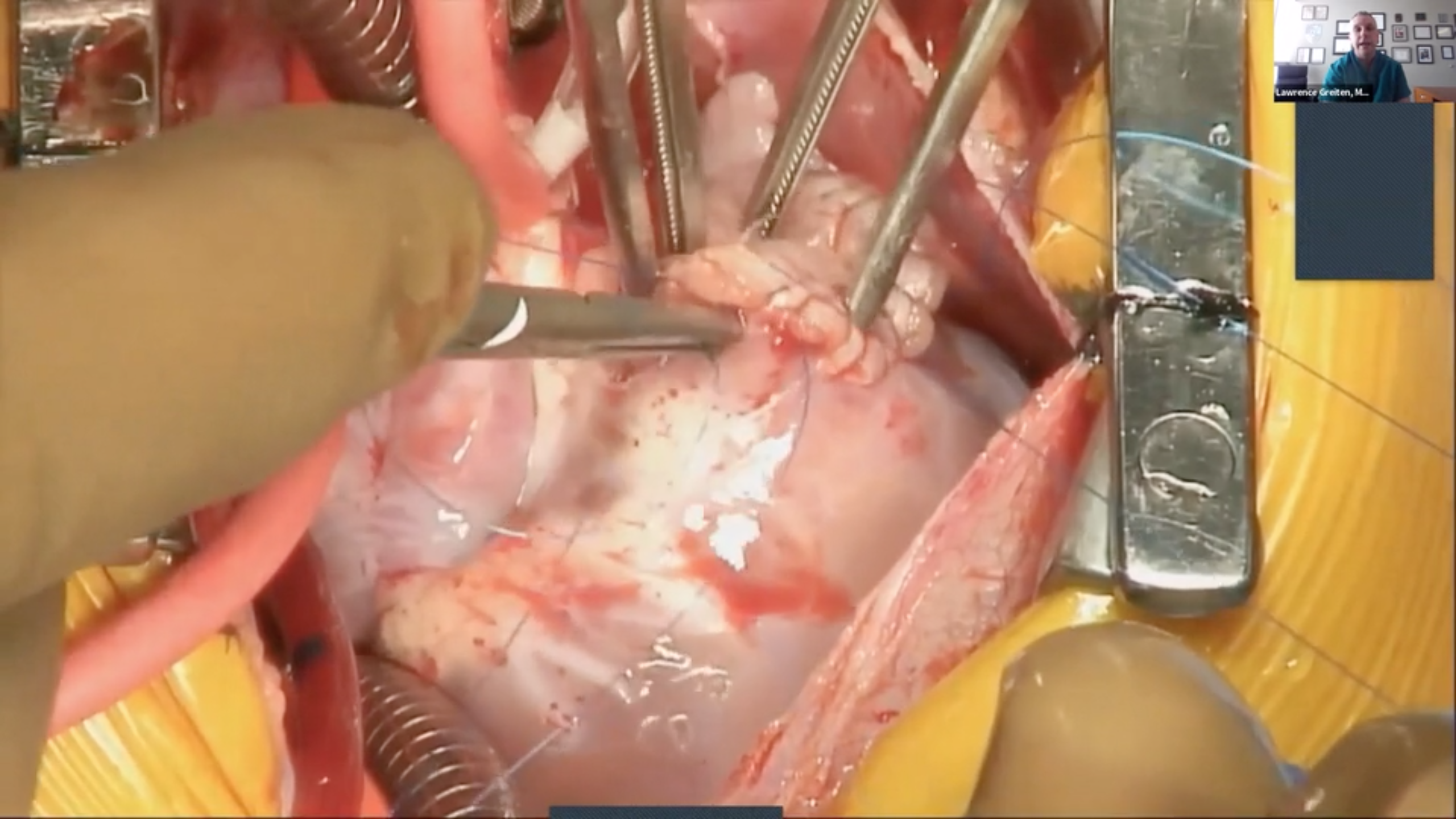
Repair of a Non-coronary Sinus of Valsalva Aneurysm Rupture
videoA brief patient history is given, followed by preoperative imaging, intraoperative repair, and postoperative imaging.
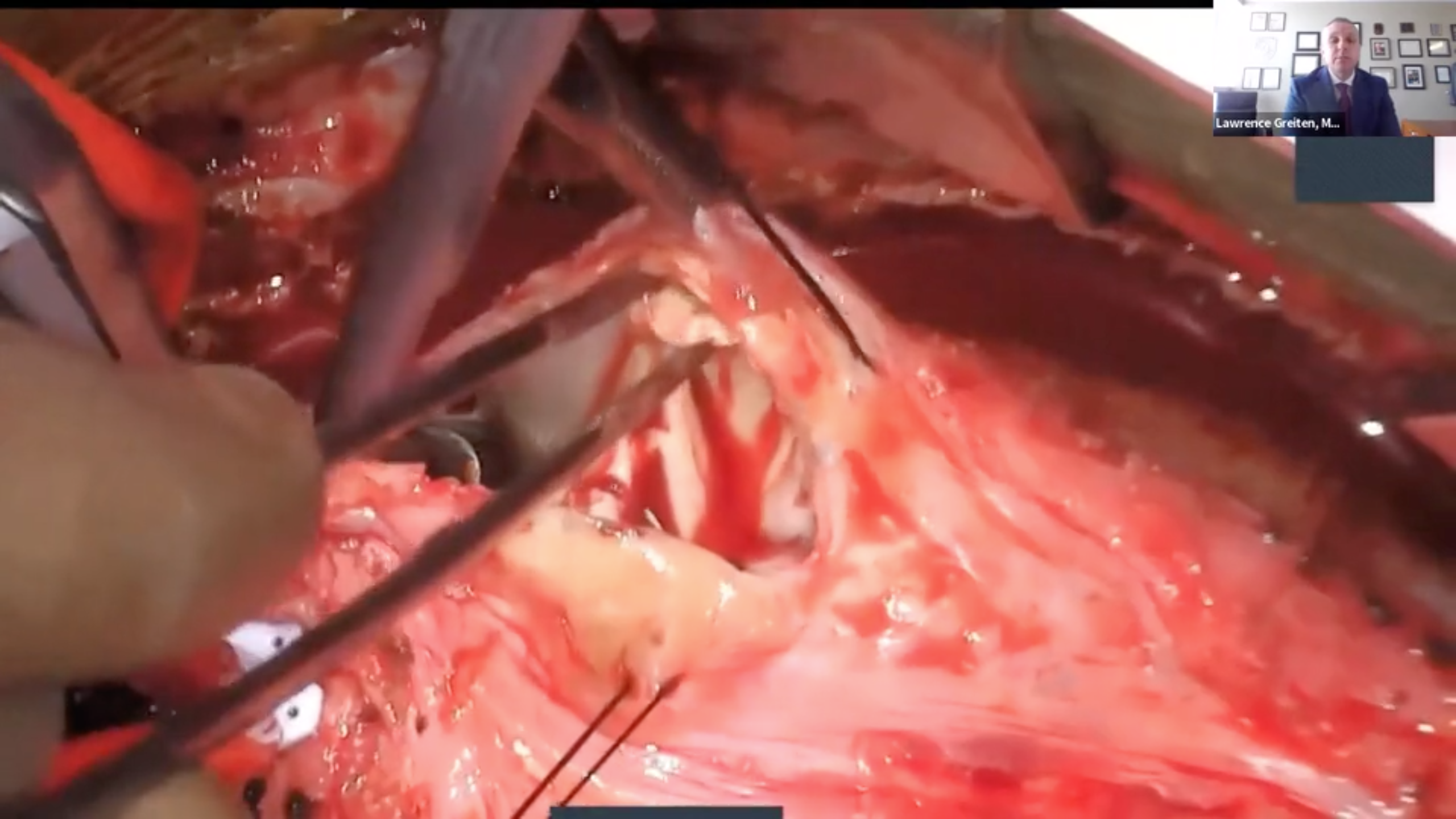
Sinus Venosus ASD Repair
videoThis video demonstrates a sinus venosus ASD repair with the two patch repair technique. Authors: Emily Goodman; Brian Reemtsen, MD; Markus Renno, MD; Christian Eisenring, ACNP-BC; Lawrence Greiten, MD University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences College of Medicine, Little Rock, AR Arkansas Children's Hospital, Little Rock, AR
Pulmonary Valve Replacement
videoThis video highlights a pulmonary valve replacement in a patient with Tetralogy of Fallot.
Complete Repair of Total Anomalous Venous Return
videoComplete repair of a total anomalous pulmonary venous return. Also shown is a primary closure of a patent foramen ovale and patent ductus arteriosus. The patient is placed on cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) in the standard fashion. The patient is then crash cooled to 20 degrees celsius with ice placed on the head and administration of steroids. Antegrade cardioplegia is then administered. The large confluent vein (vertical vein) is dissected and an arteriotomy is made, a subsequent atriotomy is made in the left atrial appendage. A side to side anastomosis using polypropylene suture in a continuous running fashion. The right atrium is then opened and the patent foramen ovale is closed. The patient was warmed to a satisfactory temperature and once adequate hemostasis was achieved the vertical vein is ligated at its insertion into the innominate vein.
Minimal incision Partial Sternotomy ASD Repair
videoThis video showcases a minimal incision, partial sternotomy exposure for complete ASD patch repair performed at Arkansas Children's Hospital.
Sinus Venosus ASD Repair
videoThis video demonstrates a sinus venosus ASD repair with the two patch repair technique. Authors: Emily Goodman; Brian Reemtsen, MD; Markus Renno, MD; Christian Eisenring, ACNP-BC; Lawrence Greiten, MD University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences College of Medicine, Little Rock, AR Arkansas Children's Hospital, Little Rock, AR
Pulmonary Valve Replacement
videoThis video highlights a pulmonary valve replacement in a patient with Tetralogy of Fallot.
Minimally Invasive Radioguided Parathyroidectomy
videoMinimally Invasive Radioguided Parathyroidectomy Author: Joshua Hagood Performing surgeon/coauthor: Brendan C. Stack, Jr., M.D., FACS, FACE Department of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, USA Overview: Primary hyperparathyroidism is a disease caused by overproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH). This condition is most commonly caused by a solitary, hyperfunctioning, adenoma among one of the four parathyroid glands. The hallmark finding of hyperparathyroidism is hypercalcemia which can manifest symptomatically as nephrolithiasis, diabetes insipidus, renal insufficiency, bone pathology, gastrointestinal symptoms, and neuropsychiatric disturbances (remembered as “Stones, Bones, Groans, and Psychiatric overtones”). Minimally invasive Radio guided Parathyroidectomy (MIRP) is a curative procedure for primary hyperparathyroidism that can use both radionuclide guidance and intraoperative PTH measurements to confirm the removal of the offending adenoma. Radionuclide guidance is performed via the injection of 99mTc-sestamibi, which is a radiomarker that sequesters within adenomatous/hypermetabolic parathyroid tissue. Intraoperatively, the amount of 99mTc-sestamibi within excised tissue can be measured with the use of a handheld gamma probe. Instrumentation: -Endotracheal Nerve Integrity Monitoring System (NIMS) -Gamma Probe -Intraoperative PTH assay equipment
Superior Rectus Recession
videoIntroduction Muscle recession is a type of strabismus surgical procedure that aims to weaken an extraocular muscle by adjusting its insertion posteriorly closer to its origin. The patient is a 14-year-old with dissociated vertical deviation, which can be corrected with recession of the superior rectus muscle. Methods A conjunctival incision is made in the fornix. Tenon's capsule is dissected to expose the superior rectus muscle. The superior rectus muscle is isolated using a Stevens tenotomy hook followed by a Jameson muscle hook. After the remaining Tenon's attachments are cleared, the muscle is secured at both poles with a double-armed 6-0 VicrylTM suture and double-locking bites. The muscle is then disinserted from the sclera with Manson-Aebli scissors. A caliper is used to mark the predetermined distance of muscle reinsertion. Next, the muscle is reattached to the sclera with partial thickness bites and then tied down to its new location. The conjunctival incision is closed with 6-0 plain gut sutures. Results No complications arose during the procedure. Postoperatively, the patient had subconjunctival hemorrhage, injection, and pain that decreased over the following week. Neomycin-polymyxin-dexamethasone drops were applied daily to prevent infection and inflammation. At the three-month follow up, the redness had resolved. The dissociated vertical deviation had improved. Conclusion Superior rectus recession is a safe procedure that can effectively treat vertical strabismus. By: Michelle Huynh College of Medicine, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA mhuynh@uams.edu Surgeons: Brita Rook, MD Arkansas Children’s Hospital – Department of Ophthalmology, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA BSRook@uams.edu Joseph Fong, MD Jones Eye Institute, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA JFong@uams.edu Video was performed at Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, AR, USA.
Redo Posterior Fossa Decompression with Duraplasty for the Treatment of Chiari Type I Malformation
videoChiari decompression is a common neurosurgical procedure. Chiari malformations present with a number of symptoms including Valsalva-induced headaches, swallowing dysfunction, and sleep apnea. Chiari malformations can also cause syringomyelia and syringobulbia. Surgical procedures used for the treatment of Chiari malformation include bone-only decompression (posterior fossa craniectomy +/- cervical laminectomy), craniectomy/laminectomy with duraplasty, and craniectomy/laminectomy/duraplasty with shrinkage or resection of the cerebellar tonsils. The procedure used depends on the specifics of the patient’s condition and the preference of the surgeon. The patient presented here had undergone a prior Chiari decompression at the age of 20 months. This was bone-only with posterior fossa craniectomy and C1-2 laminectomy. The dura was not opened due to the presence of a venous lake. He initially had improvement in his symptoms. However, his headaches and snoring recurred, balance worsened, and dysphagia never improved. Therefore, a repeat Chiari decompression at the age of 28 months was performed as presented here.
Microdebrider Assisted Lingual Tonsillectomy
videoMicrodebrider Assisted Lingual Tonsillectomy Adrian Williamson, Michael Kubala MD, Adam Johnson MD PhD, Megan Gaffey MD, and Gresham Richter MD The lingual tonsils are a collection of lymphoid tissue found on the base of the tongue. The lingual tonsils along with the adenoid, tubal tonsils, palatine tonsils make up Waldeyer’s tonsillar ring. Hypertrophy of the lingual tonsils contributes to obstructive sleep apnea and lingual tonsillectomy can alleviate this intermittent airway obstruction.1,2 Lingual tonsil hypertrophy can manifest more rarely with chronic infection or dysphagia. A lingual tonsil grading system has been purposed by Friedman et al 2015, which rates lingual tonsils between grade 0 and grade 4. Friedman et al define grade 0 as absent lingual tonsils and grade 4 lingual tonsils as lymphoid tissue covering the entire base of tongue and rising above the tip of the epiglottis in thickness.3 Lingual tonsillectomy has been approached by a variety of different surgical techniques including electrocautery, CO2 laser, cold ablation (coblation) and microdebridement.4-9 Transoral robotic surgery (TORS) has also been used to improve exposure of the tongue base to perform lingual tonsillectomy.10-13 At this time, there is not enough evidence to support that one of these techniques is superior. Here, we describe the microdebrider assisted lingual tonsillectomy in an 8 year-old female with Down Syndrome. This patient was following in Arkansas Children's Sleep Disorders Center and found to have persistent moderate obstructive sleep apnea despite previous adenoidectomy and palatine tonsillectomy. Unfortunately, she did not tolerate her continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) device. The patient underwent polysomnography 2 months preoperatively which revealed an oxygen saturation nadir of 90%, an apnea-hypopnea index of 7.7, and an arousal index of 16.9. There was no evidence of central sleep apnea. The patient was referred to otolaryngology to evaluate for possible surgical management. Given the severity of the patient’s symptoms and clinical appearance, a drug induced sleep state endoscopy with possible surgical intervention was planned. The drug induced sleep state endoscopy revealed grade IV lingual tonsil hypertrophy causing obstruction of the airway with collapse of the epiglottis to the posterior pharyngeal wall. A jaw thrust was found to relieve this displacement and airway obstruction. The turbinates and pharyngeal tonsils were not causing significant obstruction of the airway. At this time the decision was made to proceed with microdebrider assisted lingual tonsillectomy. First, microlaryngoscopy and bronchoscopy were performed followed by orotracheal intubation using a Phillips 1 blade and a 0 degree Hopkins rod. Surgical exposure was achieved using suspension laryngoscopy with the Lindholm laryngoscope and the 0 degree Hopkins rod. 1% lidocaine with epinephrine is injected into the base of tongue for hemostatic control using a laryngeal needle under the guidance of the 0 degree Hopkins rod. 1. The 4 mm Tricut Sinus Microdebrider blade was set to 5000 RPM and inserted between the laryngoscope and the lips to resect the lingual tonsils. Oxymetazoline-soaked pledgets were used periodically during resection to maintain hemostasis and proper visualization. A subtotal lingual tonsillectomy was completed with preservation of the fascia overlying the musculature at the base of tongue. She was extubated following surgery and there were no postoperative complications. Four months after postoperatively the patient followed up at Arkansas Children's Sleep Disorders Center and was found to have notable clinical improvement especially with her daytime symptoms. A postoperative polysomnography was not performed given the patient’s clinical improvement.
Cranioplasty for Sagittal Craniosynostosis
videoCranioplasty with barrel stave osteotomies to treat sagittal suture craniosynostosis.
Laparoscopic Orchiopexy: Use of a Hitch Stitch
videoContributors: John Paddack (University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences) INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVES: The percutaneous hitch stitch, a commonly described technique for elevation of the ureteropelvic junction during laparoscopic pyeloplasty, allows for easier dissection and suturing. We have adapted this technique to laparoscopic orchiopexy. METHODS: The technique described was used for testicular retraction during three consecutive cases of right-sided intraabdominal testicle RESULTS: There were three cases of non palpable testicle, mean age 31 months (range 22-42). Testicles were all within 3 cm of internal ring on laparoscopy. In all cases, testicle was placed in subdartos pouch in single stage, without division of the spermatic vessels. There were no complications. CONCLUSIONS: The percutaneous hitch stitch is a simple modification to the traditional laparoscopic orchiopexy. It provides atraumatic retraction of the intraabdominal testicle and facilitates dissection of spermatic vessels from the posterior peritoneum. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.17797/n1nnrufxpt
Laparoscopic Transposition of Lower Pole Crossing Vessels or 'The Vascular Hitch'
videoContributors: John Loomis (Texas A&M Health Science Center) Purpose: Relief of UPJ obstruction Instruments: da Vinci Robotic Surgical System Landmarks: Retropertionem, ureters, kidney, lower pole crossing vessel Procedure: The laparoscopic transposition of lower pole crossing vessels, or "vascular hitch", has been successfully used to relieve purely extrinsic ureteropelvic junction obstruction in both adults and children. This case describes the surgical steps for successfully completing this technique. Our patient is a 7 year old female. After induction of general anesthesia, the patient is placed in the right or left lateral decubitus postion (depending on the affected kidney). Access to the abdomen is accomplished with an infraumbilical incision utilizing a Veress needle, with insufflation and saline drop test. A 12mm port is placed in this incision and 2 robotic ports are placed under direct supervision, one in the midline of the suprapubic region and the other in the midline of the epigastric region, with an additional 5mm assistant port. Release of the liver or splenic attachments, with mobilization of the right and left colon, allows for exposure. After doing so, dissection into the retroperitoneum reveals the ureter, which can then be followed to the UPJ and the vessels of interest. Careful dissection of these vessels, the ureter, and lower pole, allows for mobilization of the crossing vessels to a more cranial point on the renal pelvis. "Hitching" of the vessels to this point is accomplished with interrupted 5-0 PDS, and allows for relief of the UPJ obstruction. The lower pole of the kidney is observed throughout to ensure adequate vascularization after hitching of the crossing blood vessels. Closure of the fascia and skin is accomplished in the usual fashion. Conflict of Interest: None References: 1. Sakoda A1, Cherian A, Mushtaq I., "Laparoscopic transposition of lower pole crossing vessels ('vascular hitch') in pure extrinsic pelvi-ureteric junction (PUJ) obstruction in children.", BJU Int. 2011 Oct;108(8):1364-1368. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10657.x 2. Gundeti MS, Reynolds WS, Duffy PG, Mushtaq I. "Further experience with the vascular hitch (laparoscopic transposition of lower pole crossing vessels): an alternate treatment for pediatric ureterovascular ureteropelvic junction obstruction.", J Urol. 2008 Oct;180:1832-1836. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2008.05.055 3. Schneider A, Ferreira CG, Delay C, Lacreuse I, Moog R, Becmeur F., "Lower pole vessels in children with pelviureteric junction obstruction: laparoscopic vascular hitch or dismembered pyeloplasty?", J Pediatric Urol. 2013 Aug;9(4):419-423. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2012.07.005 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.17797/maqcmavan0
Ear Tube Removal and T-tube Replacement
videoContributors: Gresham T. Richter (University of Arkansas for the Medical Scienc) 1) Purpose: Untreated Eustachian Tube dysfunction can lead to retraction of the tympanic membrane (TM) and, eventually, an atelectatic middle ear. The insertion of a tympanostomy tube attempts to equalize the air pressure of the middle ear with the environment, allowing for the stabilization of the TM. Bobbin style tubes have an average extrusion time of less than a year while T-tubes remain in place longer but risk residual perforation. (1) 2)Instruments: Rigid endoscopes were used to direct and record the procedure with standard video monitoring. Straight cupped forceps were used to debride the external auditory canal. A myringotomy knife was used to make the myringotomy. 3) Landmarks: After debridement of cerumen, the handle of the malleus and the incudostapedial joint are clearly visualized as indicated with titles in the video. Note that the patient's tympanic membrane shows an incudostapediopexy and deep retraction which is not the typical tympanic membrane position. 4) Procedure: Cerumen is debrided from the EAC. A myringotomy knife is used to enter the middle ear space which is suctioned. A t-tube is placed, and the position is confirmed. 5) Conflict of Interest and Source of Funding The authors have no financial disclosures. 6) References 1. Weigel MT, Parker MY, Goldsmith MM, Postma DS, Pillsbury HC. "A prospective randomized study of four commonly used tympanostomy tubes." The Laryngoscope. 1989 Mar;99(3):252-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1288/00005537-198903000-00003 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.17797/7zpuk5q5r6
Open Surgical Release of Stenosing Tenosynovitis (a.k.a. Trigger Finger)
videoContributors: James Kee In this video, we show the open surgical release of the A1 pulley to restore movement and alleviate triggering in a patient with stenosing tenosynovitis, or trigger finger. DOI #: https://doi.org/10.17797/punju11l92
Open Carpal Tunnel Release
videoContributors: Theresa O. Wyrick This video shows the open surgical release of the carpal tunnel for relief of compressive median neuropathy at the wrist or carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). DOI: https://doi.org/10.17797/2ddezhnxdf
Fronto-Orbital Advancement and Cranial Vault Remodeling for Metopic Craniosynostosis
videoContributors:Michael Golinko, MD, MA, Eylem Ocal, MD and Kumar Patel, PA Premature metopic suture fusion is corrected using fronto-orbital advancement and cranial vault remodeling to open the fused suture and allow for adequate brain growth. DOI#: https://doi.org/10.17797/hg9xbuxoms
Excision of Thyroglossal Duct Cyst
videoContributors: Juliana Bonilla-Velez and Gresham Richter This patient presented with an anterior neck mass that was mobile with tongue movement. This is consistent with a thyroglossal duct cyst. The following video demonstrates the excision of a thyroglossal duct cyst using the Sistrunk procedure. DOI#: http://dx.doi.org/10.17797/oelc9n6wlc
Alopecia Excision and Repair
videoContributors: Michael Golinko and Kumar Patel Removal of an approximately 5 cm congenital alopecia using an O to Z or yin-yang flap method. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.17797/rbbu00mhp0
Pediatric Trigger Thumb Release
videoVideos: Theresa Wyrick and Asa Shnaekel In this video, we show the open surgical release of the A1/proximal transverse pulley in the thumb to restore movement in a patient with a thumb interphalangeal joint flexion deformity consistent with pediatric trigger thumb. DOI# http://dx.doi.org/10.17797/b70rwrfg0p
Bilateral Sagittal Spilt Osteotomy and Genioplasty in Patient with Lymphatic Malformation
videoContributors: Michael Golinko, MD, John Jones, MD, DMD, Kumar Patel, PA Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy and genioplasty in 5y/o girl with lymphatic malformation. DOI#: https://doi.org/10.17797/hlo056ep2r
LeFort I Osteotomy and Advancement in Patient with Maxillary Hypoplasia
videoContributors: Michael Golinko, Kumar Patel and Bridget O'Leary LeFort I osteotomy and advancement in 18y/o female patient with maxillary hypoplasia DOI: https://doi.org/10.17797/1cu3tz50yf
Bilateral Cleft Lip Repair
videoContributors: Larry Hartzell Repair of the bilateral cleft lip deformity can be challenging to the cleft and craniofacial surgeon. The goals of an acceptable repair must include precise continuity of the cupid's bow, maximizing philtral length, and establishing a mucosa lined sulcus. We present an example of a repair of the bilateral incomplete lip as described by Millard. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.17797/qefi9lqbam
Congenital Nasal Pyriform Aperture Stenosis (CNPAS): Sublabial Approach to Surgical Correction
videoCongenital nasal pyriform aperture stenosis (CNPAS) is defined as inadequate formation of the pyriform apertures forming the bony nasal openings resulting in respiratory distress and cyanosis soon after birth. Some clues such as worsening distress during feeding and improvement during crying may indicate a nasal cause of respiratory distress rather than distal airway etiology. Inability or difficulty passing a small tube through the nasal cavities may suggest CNPAS. The presenting clinical features of CNPAS can be similar to other obstructive nasal airway anomalies such as choanal atresia. Diagnosis is confirmed via CT scan with a total nasal aperture less than 11mm. CNPAS may occur in isolation or it may be a sign of other developmental abnormalities such as holoprosencephaly, anterior pituitary abnormalities, or encephalocele. Some physical features of holoprosencephaly include closely spaced eyes, facial clefts, a single maxillary mega incisor, microcephaly, nasal malformations, and brain abnormalities (i.e. incomplete separation of the cerebral hemispheres, absent corpus callosum, and pituitary hormone deficiencies). It is important to rule out other associated abnormalities to ensure optimal treatment and intervention. Conservative treatment of CNPAS includes humidification, nasal steroids, nasal decongestants and reflux control. Failure of conservative treatment defined by respiratory or feeding difficulty necessitates more aggressive intervention. The most definitive treatment for CNPAS is surgical intervention to enlarge the pyriform apertures. Contributors: Adam Johnson MD, PhD Abby Nolder MD
Mandibular Distraction for Micrognathia in a Neonate
videoIntroduction Patients with Pierre-Robin Sequence (PRS) suffer from micrognathia, glossoptosis, and upper airway obstruction, which is sometimes associated with cleft palate and feeding issues. To overcome these symptoms in our full-term male neonate patient with PRS, mandibular distraction osteogenesis was performed. Methods The patient was intubated after airway endoscopy. A submandibular incision was carried down to the mandible. A distractor was modified to fit the osteotomy site that we marked, and its pin was pulled through an infrauricular incision. Screws secured the plates and the osteotomy was performed. The mandible was distracted 1.8 mm daily for twelve days. Results During distraction, the patient worked with speech therapy. Eventually, he adequately fed orally. He showed no further glossoptosis or obstruction after distraction was completed. Conclusion In our experience, mandibular distraction is a successful way to avoid a surgical airway and promote oral feeding in children with PRS and obstructive symptoms. By: Ravi W Sun, BE Surgeons: Megan M Gaffey, MD Adam B Johnson, MD, PhD Larry D Hartzell, MD Department of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, USA Arkansas Children's Hospital, Little Rock, AR, USA Recruited by: Gresham T Richter, MD
Le Fort I Osteotomy with placement of Distractor
videoOur patient is a 20 year old boy with severe maxillary hypoplasia with a history of bilateral cleft lip and palate. We performed a maxillary advancement with distraction osteogenesis. Nikhil Kamath, BS Aaron Smith, MD Michael S. Golinko, MD Kumar Patel, PA-C
Revision Facial Bipartition Osteotomy
videoRevision Facial Bipartition Osteotomy in 14y/o Female. Contributors: Aaron Smith, MD; Kumar Patel, PA; Ashley Bartels, BS; Rongsheng Cai, MD; Roop Gill, MD
Excision of Macrocystic Lymphatic Malformation
videoIntroduction Lymphatic malformations (LM) are composed of dilated, abnormal lymphatic vessels classified as macrocystic (single or multiple cysts >2 cm3), microcystic (<2 cm3), or mixed. This patient is a 5-month-old with a right neck mass consistent with macrocystic lymphatic malformation on MRI. This low-flow vascular malformation required surgical intervention. Methods The site was marked in a natural skin crease. Subplatysmal flaps were raised and malformation was immediately encountered. Blunt soft tissue dissection was performed immediately adjacent to the mass to reflect tissue off the fluid-filled lesion. Neurovascular structures were preserved in this process. Mass was removed in total and Penrose drain and neck dressing were placed. Results A complete resection was performed. LM was confirmed on pathology. Patient is doing well with no deficits noted. The drain was removed after 1 week. One-month follow-up showed no recurrence. Conclusion Macrocystic lymphatic malformations are amenable to surgical resection at low risk and without recurrence. By: Ravi W Sun, BE Surgeons: Luke T Small, MD Gresham Richter, MD Department of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, USA Arkansas Children's Hospital, Little Rock, AR, USA Recruited by: Gresham T Richter, MD
Split Thickness Skin Graft
videoSkin grafting involves closure of an open wound using skin from another location which is transferred without its own vascular blood supply, relying on the vascular supply of the wound bed for survival. Skin grafts can be split thickness grafts that may involve meshing the donor skin in order to cover a proportionally larger area than the donor skin may have allowed. Besides the ability to cover a large area, a split thickness skin graft (STSG) allows for egress of fluids thereby maximizing close contact between the wound and the graft, which is necessary for vascularization and survival of the graft. A STSG can be taken at a variety of thicknesses but at any level taken, part of the donor dermis is left intact. Other options for skin grafts include full thickness grafts and biomedical grafts such as Integra. Full thickness skin grafts (FTSG) take the dermis as well as epidermis, usually covering smaller areas. FTSG has reduced contracture and often a better color match compared to STSG, but can have reduced survival due to increased thickness of tissue. The decision of the type of graft used in the procedure is made in accordance with the needs of the recipient site, the likelihood of graft take, and the availability of donor skin. The patient may either go home after the procedure with small areas of skin grafting with instructions for immobilization and elevation of the grafted area. The patient may be admitted depending on the patient’s general health status and the wound. Shear forces are avoided to the grafted area, and the donor site dressings may require prn changes due to fluid leakage until the skin epithelium regenerates from residual dermal structures. In the case presented in this video, a 12 year old girl was victim to a degloving injury of the left dorsal foot secondary to a motor vehicle accident. A STSG was determined appropriate for wound coverage as her wound bed had granulated in very well, covering all critical structures and providing a healthy bed for graft take. Linda Murphy MA Roop Gill, MD
Tympanoplasty with tragal cartilage graft, postauricular approach
videoTympanoplasty with tragal cartilage graft, postauricular approach Blake Hollowoa, Michael Kubala, Gresham Richter. Introduction Tympanic membrane (TM) perforations arise from multiple conditions including acute otitis media, barotrauma, chronic eustachian tube dysfunction, or as a complication of pressure equalization (PE) tube insertion. Most perforations heal spontaneously or with conservative measures such as ototopical drops and dry ear precautions. Perforations that do not heal can lead to conductive hearing loss, chronic infection, or cholesteatoma. A 6-year-old patient with a persistent TM perforation presented with otalgia and otorrhea. A tympanoplasty with a tragal cartilage graft was performed to repair the patient’s TM perforation. Methods The patient was intubated and the operation carried out under general anesthesia. Facial electrodes were inserted for facial nerve monitoring. The patient was prepped and draped in sterile fashion. The external canal was suctioned and irrigated. A tragal incision was then made to harvest a 1 cm piece of cartilage for the TM graft. The tragal incision was closed with monocryl suture. A postauricular incision was made in the natural skin crease to expose the posterior canal. Canal incisions were made to enter the external canal. A tympanomeatal flap was elevated until the middle ear was entered. The previously harvested tragal cartilage graft was inserted medial to the native TM perforation. Gel-Foam was inserted medial to the graft for support. Tragal perichondrium was inserted lateral to the tragal cartilage graft. Gel-Foam was then inserted lateral to the graft for support. The periosteum and postauricular incision were closed with vicryl suture. The external canal was inspected, then antibiotic ointment and an ear wick was inserted. The patient was dressed using a Glasscock dressing. Results The patient was discharged the same day and seen in clinic two weeks from his surgery. The incisions were healing well with no indications of infection or wound dehiscence. His pain was resolved and an appointment for formal audiology was scheduled for a 3-month follow-up visit. Conclusion Tympanoplasty with a tragal cartilage graft using a postauricular approach is a successful method to surgically correct persistent tympanic membrane perforations.
Superiorly Based Pharyngeal Flap for Velopharyngeal Dysfunction
videoVelopharyngeal dysfunction (VPD) refers to the improper control of airflow through the nasopharynx. The term VPD denotes the clinical finding of incomplete velopharyngeal closure. Other terms used to describe VPD include velopharyngeal insufficiency, inadequacy and incompetence. However, the use of VPD has gained popularity over these terms as they may be used to infer a specific etiology of impaired velopharyngeal closure.1 Control of airflow through the nasopharynx is dependent on the simultaneous elevation of the soft palate and constriction of the lateral and posterior pharyngeal walls. Disruptions of this mechanism caused by structural, muscular or neurologic pathology of the palate or pharyngeal walls can result in VPD. VPD can result in a hypernasal voice with compensatory misarticulations, nasal emissions and aberrant facial movements during speech.2 The assessment of velopharyngeal function is best preformed by a multispecialty team evaluation including speech-language pathologists, prosthodontists, otolaryngologists and plastic surgeons. The initial diagnosis of VPD is typically made with voice and resonance evaluation conducted by a speech-language pathologist. To better characterize the patient’s VPD, video nasopharyngeal endoscopy or speech videofluoroscopy can be used to visualize the velopharyngeal mechanism during speech. VPD may first be managed with speech-language therapy and removable prostheses. For those who are good surgical candidates and do not fully respond to speech-language therapy, surgical intervention may be pursued. Surgical management of VPD is most commonly accomplished by pharyngeal flap procedures or sphincter pharyngoplasty. In this video, a superiorly based pharyngeal flap with a uvular mucosal lining flap was preformed for VPD in a five-year-old patient with 22q11 Deletion Syndrome and aberrantly medial internal carotid arteries.
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy for Non-communicating, Obstructive Hydrocephalus
videoAn endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) can be a sufficient alternative to a cerebral shunt in the treatment of noncommunicating forms of hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus can present with numerous signs and symptoms, including headache, vomiting, neck pain, macrocephaly, and vision impairment. Surgical procedure includes entrance of the lateral ventricles through a bur hole, and blunt/cautery fenestration of the third ventricular floor, which lies between the mamillary bodies and tuber cinereum. Choroid plexus cautery has been noted in the literature as being a viable addition to the procedure, in which a reduction in CSF production is achieved. Though, exact surgical procedure is left to the discretion of the surgeon. The patient presented is a 30-month-old boy with non-communicating obstructive hydrocephalus secondary to congenital aqueductal stenosis. The patient has a history of progressive developmental delays, balance issues, and increased seizure frequency from a known seizure disorder. Therefore, an endoscopic third ventriculostomy via right frontal approach was elected. Authors: William Fuell, Marcus Stephens M.D., Eylem Ocal M.D. Institutions: Arkansas Children's Hospital, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Excision of Macrocystic Lymphatic Malformation
videoThis patient is a 9-month-old with a macrocystic lymphatic malformation (LM) of the left neck. LMs, the second most common type of head and neck vascular malformation, are composed of dilated, abnormal lymphatic vessels thought to occur due to abnormal development of the lymphatic system. A complete resection was performed, and LM was confirmed by pathology. Soft tissue dissection was performed immediately adjacent to the mass to reflect tissue off the fluid-filled lesion. Neurovascular structures were preserved in this process.
Implantation of Tissue Expander in Poland Syndrome Patient
videoThis patient is a seventeen-year-old female with Poland syndrome, resulting in a hypotrophic left pectoralis major muscle and rib anomalies. A tissue expander is implanted on the left side to increase the capacity of the left breast tissue in order to make room for a future, permanent implant.
Orbital Decompression through Conjuctival and Lynch Incisions
videoSurgical orbital decompression for proptosis secondary to Graves' Disease.
Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty
videoIntroduction: Cosmetic Upper Blepharoplasty involves removing excess skin from the upper eyelid to enhance the appearance of the upper eyelids. Methods: Markings were made for the inferior incision on the upper eyelid between 8-10 mm above the upper lash line. Forceps are used to pinch the excess upper eyelid skin in the middle, nasal, and temporal, aspects of the upper eyelid. Markings are then made superiorly at the middle, nasal, and temporal points and are connected. Toothed forceps are used to pinch the excess upper eyelid skin, using the markings as a guide. Iris scissor is used to excise the pinched excess skin and the underlying orbicularis muscle. The skin between the two eyelids was closed. Conclusions: In our experience, cosmetic upper blepharoplasty is an efficient way to enhance the appearance of the eyes. By: Peyton Yee, Addison Yee Surgeon: Suzanne Yee, MD, FACS Dr. Suzanne Yee Cosmetic and Laser Surgery Center, Little Rock, AR, USA Recruited by: Gresham T Richter, MD
Bilateral Wise Pattern Inferior Pedicle Reduction Mammoplasty
videoWe present a 16-year-old female with hypertrophic breasts of bra size 38H, bra strap grooving, and worsening back and posterior shoulder pain limiting activity and affecting posture, who underwent bilateral reduction mammoplasty using the Wise pattern inferior pedicle technique. 998 g of tissue was removed from the patient’s right breast, and 852 g of tissue was removed from the patient’s left breast. The procedure was uncomplicated; however, the postoperative period was complicated by minor skin breakdown at the most inferior portion of the incision along the inframammary fold, as well as some serous drainage that shortly resolved with treatment. Overall, the patient is satisfied with the results of the reduction. She reports comfortably wearing size 38C bras and has noticed significant improvement in back pain, shoulder pain, and bra strap grooving six months after the procedure.
Excision of a Preauricular Cyst
videoBackground Preauricular cysts are a subset of asymptomatic, dome-shaped lesions referred to as epidermoid cysts. Cysts vary in size and have the ability to grow in diameter over time. These cysts can occur anywhere on the body and usually contain keratin. Upon examination of a suspected cyst, different characteristics can specify its type. Dermoid cysts are typically odorous lesions found around the eyes or on the base of the nose. If the cyst did not originate from sebaceous glands, it is not deemed a sebaceous cyst. Typically, surgical intervention is required to fully remove the cyst and prevent further infections or growth. Introduction The video shows an 18-year-old female who presented with a preauricular cyst near her left ear. Upon history and physical examination, the mass was predicted to be a dermoid cyst rather than a sebaceous cyst. Surgical recommendations were given to perform an excisional biopsy of the cyst. The excision is displayed step-wise in the video. Methods A 2 cm incision was made just posterior to the lesion with a 15 blade scalpel. Dissection was carried with a sharp hemostat down the level of the parotid fascia. A 1 cm cystic structure was found adherent to the overlying dermis. An elliptical incision was then made over the mass and it was removed with the adherent overlying skin. The wound was then irrigated. Wound was closed in 3 layers. First, the deep layer was closed with 5-0 PDS in interrupted fashion, followed by 5-0 monocryl in running subcuticular fashion, followed by Dermabond Results The patient was returned to the care of anesthesia where she was awoken, extubated, and transported to PACU in stable condition. The patient tolerated the procedure well and was discharged the same day. The specimen was sent for pathological analysis. The pathology report showed that the mass was an epidermal inclusion cyst.
Bilateral Subcranial Le Fort III Osteotomies with Midface Distraction – A Surgical Review
videoIn this video, we showcase the bilateral subcranial Le Fort III osteotomies with midface distraction using Kawamoto distractors. The surgery was performed in a 4-year-old boy with Crouzon Syndrome to correct his severe proptosis, increase the nasopharyngeal airway space and improve his severe negative overjet. Internal distractors were chosen to achieve maximum correction at this age. The patient undergoing surgery had no intraoperative or postoperative complications. A full separation of his facial bones was achieved. The patient had an uneventful recovery period, and there was a significant improvement in his proptosis and malocclusion. Santiago Gonzalez, BS, BA (1); Michael Golinko, MD, MS (2) 1. University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences – College of Medicine 4301 W. Markham, #550 Little Rock, AR 72205 2. Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Department of Plastic Surgery 2900 Children’s Way, 9th Floor Doctor’s Office Tower Nashville TN 37232
Pediatric Tracheostomy
videoThe following video demonstrates the authors' method for performing a tracheostomy in a pediatric patient. Details of important anatomical landmarks and surgical technique are demonstrated in the video. Authors: Chrystal Lau, BA. University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. Brad Stone, BA. University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. Austin DeHart, MD. Arkansas Children's Hospital. Michael Kubala, MD. University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. Gresham Richter, MD. Arkansas Children's Hospital.
Inferior Turbinate Trim
videoBasic Info: A 14-year-old male presented with chronic nasal obstruction and awake stertor. It was discovered that the patient had severe bilateral turbinate hypertrophy. A trial of Flonase and antihistamine was attempted with no improvement. It was recommended that the patient undergo a bilateral nasal turbinate reduction. This procedure is displayed step-wise in the video. Introduction: Chronic nasal obstruction can be caused by inferior turbinate hypertrophy. This video portrays a surgical treatment for turbinate hypertrophy, a turbinate trim with a microdebrider blade. Methods: An Afrin pledget was inserted into each nostril and lidocaine was injected into each inferior turbinate. Each turbinate was medially fractured using a freer. The microdebrider blade was used to trim the inferior 1/3 of each turbinate. A freer was used to out-fracture each inferior turbinate. Afrin pledgets were inserted into each nostril for hemostasis. Results: The inferior one-third of each inferior turbinate was removed via a microdebrider. Patient was sent to recovery in good condition, and Afrin pledgets were removed in recovery once hemostasis was achieved. No adverse reactions were reported by the surgeon or patient. Conclusion: Chronic nasal obstruction can be significantly improved by an inferior turbinate trim and out-fracture. Author: Merit Turner, BS, BS Surgeon: Gresham T. Richter, MD Institutions: Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, AR University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR
Phacoemulsification of Nuclear Cataract and Intraocular Lens Implantation
videoCataract surgery is an appropriate option to consider when a patient’s visual function is no longer able to support their desired activities or when it becomes a detriment to their health and quality of life. Phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation is the most common procedure used to restore vision in patients with cataracts; it has been shown to restore vision to 20/40 or better in over 95% of cases [2] . The procedure uses an ultrasonic handpiece to fragment, emulsify, and aspirate an opacified lens all through a small incision in the cornea. A new intraocular lens made of acrylic is inserted into the remaining lens capsule and replaces the cataract. This outpatient surgery is typically sutureless and completed in 10-20 minutes. This case highlights a patient with a nuclear sclerotic cataract who elected for phacoemulsification extraction with intraocular lens implantation. The video showcases the proper placement of cataract removal instruments and phaco handpiece, completion of the most critical step of the procedure—the capsulorhexis and highlights proper placement of the intraocular lens. Authors Adam Neuhouser, Medical Student, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, ajneuhouser@uams.edu. Victoria Ly, Medical Student, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, vly@uams.edu. Ahmed A. Sallam, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Ophthalmology, Jones Eye Institute. asallam@uams.edu
Lateral Rectus Plication
videoIntroduction Muscle plication is a type of strabismus surgery that aims to tighten an extraocular muscle by partially folding the muscle under or over itself without disinsertion. The patient is a 14-year-old with alternating esotropia, who previously had a medial rectus recession. Therefore, she underwent plication of the lateral rectus muscle for this procedure. Methods A conjunctival incision is made in the fornix. Tenon's capsule is dissected to expose the lateral rectus muscle. The lateral rectus muscle is isolated using a Stevens tenotomy hook followed by a Jameson muscle hook. A Stevens tenotomy hook is used to sweep around the muscle to confirm the location of the muscle pole. A caliper is used to mark the predetermined amount of plication, starting at the muscle insertion and marking further posteriorly on the muscle. The muscle is then secured at the location marked by the caliper with a double-armed 6-0 VicrylTM suture with a central bite and double-locking bites at each pole of the muscle. Plication is achieved by bringing the muscle anteriorly and attaching it to the sclera adjacent to the muscle insertion with half-scleral depth bites in crossed-swords fashion. The muscle is tied down to its new location and 6-0 plain gut sutures are used to close the conjunctival incision. Results No complications arose during the procedure. Postoperatively, the patient had subconjunctival hemorrhage, injection, and pain that decreased over the following week. Neomycin-polymyxin-dexamethasone drops were applied daily to prevent infection and inflammation. At the three-month follow up, the redness had resolved. The alternating esotropia had improved. Conclusion Lateral rectus plication is a safe procedure that can effectively treat esotropia. By: Michelle Huynh College of Medicine, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA mhuynh@uams.edu Surgeons: Brita Rook, MD Arkansas Children’s Hospital – Department of Ophthalmology, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA BSRook@uams.edu Joseph Fong, MD Jones Eye Institute, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA JFong@uams.edu Video was performed at Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, AR, USA.
Laparoscopic Right Salpingo-oophorectomy in a patient at 17 weeks gestation
videoIntroduction: The prevalence of adnexal masses in pregnancy ranges from 0.05 to 2.4 percent and approximately 1 to 6 percent of these masses are malignant. Patients typically present on prenatal ultrasound asymptomatically but some can have abdominal and back pain as well. Concerns for the fetus and complications in pregnancy cause surgeries to be postponed until after delivery; however, some adnexal masses require evaluation for malignancy. We present a case of a 28-year-old female with a cystic adnexal mass that required laparoscopic salpingo-oophorectomy at 17 weeks gestation. Methods: After the patient was prepped and draped,the initial laparoscopic port was placed in the left upper quadrant, 3 cm below the costal margin and in the midclavicular line. This area, known as Palmer’s point, was chosen as the site for the initial port placement in order to avoid the gravid uterus. After intraperitoneal placement, the abdomen was insufflated with CO2 gas. Laparoscopic ports were placed at the umbilicus and in the right lower quadrant under direct visualization. The port placed at the umbilicus was an Applied Medical GelPOINT Advanced Access Platform. The entire abdominal and pelvic cavities were examined for any lesions. An initial washing was done to examine for malignant cells. The left ovary was examined and determined to be normal. The right ovary was noted to be enlarged, to approximately 10 cm, and was displaced into the posterior cul de sac. Next the infundibulopelvic ligament, broad ligament, ovarian vessels, and ureter are identified. The ureter, which is typically able to be identified at the pelvic brim where it crosses over the bifurcation of the iliac vessels and passes medially, was noted to be well below the plane of dissection. If the ureter is unable to be located trans-peritoneally, a peritoneal incision can be made parallel to the ovarian vessels and the ureter located retroperitoneally in the medial leaflet of the broad ligament. The right fallopian tube and right utero-ovarian ligament were transected using the Ligasure bipolar device. We evaluated for hemostasis of the pedicles. The right suspensory ligament of the ovary containing the ovarian vessels was then isolated and cauterized and transected using the Ligasure bipolar device. A laparoscopic retrieval bag was introduced through the GelPOINT advanced access platform, the specimen was placed in the bag, and then the bag was brought to the surface of the patient's abdomen. We were able to drain straw colored fluid from the cyst with the cyst contained safely within the bag. The remainder of the specimen was then able to be removed, contained within the bag. The patient’s abdomen was deflated and the ports were removed. The fascia at the umbilicus was closed with an 0 Vicryl (polyglactin) suture so as to avoid herniation at the site of the larger incision accommodating the GelPOINT. The rest of the ports were closed using subcuticular sutures. Discussion: Pathology revealed a mature cystic teratoma. The patient was discharged home on the same day of surgery with no complications. Fetal heart tones were within normal limits pre- and post-procedure. Laparoscopic surgery is a safe treatment for pregnant women with non-obstetrical surgical issues, including adnexal masses.
Scleral Fixation of Intraocular Lens Using Gore-Tex Suture
videoThis video demonstrates scleral-fixation of an intraocular lens with GoreTex suture. The surgery was performed by Dr. Ahmed Sallam MD, PhD at the Jones Eye Institute at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. The authors of the video are Victoria Ly, Adam Neuhouser, and Ahmed Sallam MD, PhD.
Right Sided Hemithyroidectomy for Benign Multinodular Goiter
videoAuthor: Joshua Hagood Performing surgeon/coauthor: Brendan C. Stack, Jr., M.D., FACS, FACE Department of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, USA
Lip Pit Excision
videoThis video shows a pediatric patient with Van der Woude syndrome. He has lip pits that are classic for this syndrome and his family desired surgical correction. This video outlines and shows the steps of the modified simple excision technique as well as discussing tips for a successful surgery.
Phacoemulsification of a cataract
videoPhacoemulsification of a cataract Samia Nawaz, John Chancellor, and Ahmed Sallam Introduction A cataract can be simply defined as clouding of the lens of the eye. As the proteins that make up the lens of the eye harden and aggregate, a cataract forms. Cataracts are attributed to cause half of vision loss in the population and are most commonly related to age, although trauma, radiation exposure, and genetics have also been implicated. Cataracts can cause visual disturbance such as faded color perception, blurry vision, reduced night vision, and the perception of seeing halos around lights. Due to these hindrances, surgery is a common approach to alleviate the problems they cause. Phacoemulsification is a technique that uses ultrasonic waves to emulsify the dysfunctional lens, and we may then replace it with a synthetic one, clarifying vision. A 55 year old patient presented with reduced visual acuity due to a cataract in their left eye. A phacoemulsification of the cataract with implantation of an intraocular lens was performed here. Methods First, the patient’s eye was anesthetized using topical anesthetic. The patient was prepped and draped using sterile technique. A knife was then inserted into the cornea 90 degrees to the presumed incision site. This is known as the primary port incision. After this, incisions are placed 45 degrees to the presumed incision site, known as the secondary port incision. Viscoelastic was then inserted into the anterior chamber. Continuous curvilinear capsulorrhexis was performed using capsulorrhexis forceps to open the anterior capsule of the eye. We began with a central linear cut, then pulled the needle in the direction of the desired tear, allowing the capsule to fold over. We had created a flap we used to gain entry to the lens. We injected salt solution under the anterior capsule in a step called hydrodissection, allowing the fluid to decompress the anterior capsule by compressing the central part of the lens. Nuclear rotation, a step which mobilizes the nucleus and minimizes the possibility of damage to the zonular fibers or posterior capsule, was then performed. Phacoemulsification was begun after this, where ultrasonic waves broke up the nucleus of the lens into smaller pieces, thereby fragmenting the cataract and emulsifying it into a mixture to be irrigated and aspirated. We then inserted an irrigation/aspiration instrument to remove residual pieces of lens cortex. The last step was insertion of the pre-folded synthetic lens. We reformed the anterior chamber with viscoelastic, and then loaded the lens in with a cartridge. It will unfold and settle into the eye with our adjustments. We then irrigated the wound to decrease leakage by swelling up the wound edges. Results The patient was discharged the same day and followed up in clinic 1 week later. The incisions were healing well with no indications of infection or wound dehiscence. Conclusion Phacoemulsification of a cataract is a successful and widely used way of alleviating reduced visual acuity as a result of cataract formation in the eye.
Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation
videoA 70-year-old male presented with persistent left-sided epistaxis, occurring 4 - 12 times a day for 3 weeks. Episodes lasted 10 - 15 minutes, but once required nasal packing at the ED. Introduction: Ligation of the sphenopalatine artery is often indicated for patients with persistent posterior epistaxis that cannot be attributed to other causes. This video demonstrates a step-wise endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation using hemoclips. Methods: In order to access the maxillary sinus cavity, a ball-tip probe was used to fracture the uncinate and a backbiter was used to remove the uncinate in its entirety. Once in the maxillary sinus, a backbiter was used to remove the tissue anterior to the normal ostium. A straight Tru-Cut was used to remove tissue posterior the natural ostium, taking down the posterior fontanelle. After this was done, a down-biter and a microdebrider blade were used to remove tissue inferior to the natural ostium towards the inferior turbinate. A caudal instrument was used to raise a subperiosteal flap just posterior to the left maxillary sinus posterior wall. Next, dissection from the inferior turbinate up to the top of the maxillary sinus was done from an inferior to superior direction, roughly 1 cm posterior to the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus. The sphenopalatine artery was seen coming out of the sphenopalatine foramen and soft tissue was dissected off this artery. Two hemoclips were placed over the entire artery. Results: The patient was sent to recovery in good condition and no adverse reactions were reported by the surgeon or patient. Surgeons: Alissa Kanaan, MD. Zachary V. Anderson, MD. Institution: Department of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences.
Hysteroscopic Treatment of Angular Pregnancy
videoA 30-year-old female underwent in-vitro fertilization and preimplantation genetic testing. The patient conceived after her first frozen embryo transfer (FET). Beta-hCG was measured at 85 and was doubling appropriately. Ultrasound showed an angular pregnancy with heart beat confirmed by MRI. The patient has a deep arcuate uterus which may have predisposed to angular pregnancy. She was given 3 doses of methotrexate unsuccessfully. Due to concern of rupture, she underwent a hysteroscopic injection of methotrexate inside the gestational sac at 7 weeks. Hysteroscopy showed the gestational sac within the angular portion of the uterus as well as the needle penetrating the gestational sac to inject the 50mg methotrexate (see video). Fetal heart rate ceased and the patient passed products of conception 1 week later. The patient had no further complications and had a normal pregnancy on her next FET that resulted in a livebirth.
Cataract Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation in a Small Pupil Case
videoIntro Phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation is the gold standard procedure for removing cataracts in developed countries. The patient is an elderly adult who underwent the surgery to alleviate visual impairment from a significant age-related mixed cataract. Before the surgery, his visual acuity in the operative eye was 20/60. Methods This video highlights the steps of cataract phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation in a small pupil case, including paracentesis, epinephrine-lidocaine (epi-Shugarcaine) injection for extra dilation and anesthesia, viscoelastic injection into the anterior chamber, capsulorrhexis, hydrodissection, phacoemulsification featuring a divide and conquer technique, cortical irrigation and aspiration, intraocular lens insertion, and wound sealing by hydration. Results No complications arose during the procedure. At the two-week postoperative follow-up, the patient’s visual acuity in the operative eye was 20/30. He denied any pain or discomfort. The visual acuity at four weeks was 20/20. The patient was pleased with results of the surgery. Conclusion Phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation is a safe and effective surgery for the management of cataracts. In the setting of a small pupil, intracameral epinephrine-lidocaine mix (epi-Shugarcaine) can be administered for extra dilation. Authors Michelle L. Huynh, BA College of Medicine, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA Joseph G. Chacko, MD Jones Eye Institute, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA Surgeon Joseph G. Chacko, MD Jones Eye Institute, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA Music Royalty Free Music from Bensound
Chalazion Incision and Curettage
videoIntro A chalazion is a lipogranulomatous inflammation of a meibomian gland in the eyelid that presents as a painless eyelid nodule or swelling. This pediatric patient presented with a chalazion that caused symptoms of eye irritation. The lesion had persisted for many months without improvement in response to warm compresses and eyelid scrubs with baby shampoo. Therefore, she underwent chalazion incision and curettage under sedation. Methods This video highlights the steps of chalazion incision and curettage. With a chalazion clamp tightened over the lesion, the eyelid is everted and an incision is made into the tarsus. A curette is used to scrape the walls of the cyst to remove the chalazion contents. At the conclusion of the procedure, the clamp is removed and pressure is applied to the area of the lesion for hemostasis. Conclusion Incision and curettage is a safe, relatively quick, and effective procedure for the management of persistent chalazia. Authors Michelle L. Huynh, BA College of Medicine, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA Muhammad Shamim, MD Jones Eye Institute, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA Christian Ponder, MD Jones Eye Institute, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA A. Paula Grigorian, MD Arkansas Children’s Hospital – Department of Ophthalmology, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA The procedure was performed at Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, AR, USA. Music by bensound.com.
Ahmed® Glaucoma Valve for Treatment of Refractory Glaucoma
videoIntroduction Intraocular pressure is the single modifiable risk factor resulting in progression of various subtypes of glaucoma. Intraocular pressure control is often achieved with topical medications, outpatient laser procedures, or minimally-invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS). This patient is a 63-year-old with traumatic glaucoma in the right eye with elevated intraocular pressure sub-optimally controlled despite maximum medical therapy (29 mmHg). His intraocular pressure must be controlled with incisional glaucoma surgery - in this case, with placement of an Ahmed Model FP7 glaucoma valve. An advantage of valved glaucoma shunts is lower risk of postoperative hypotony-related complications compared to non-valved glaucoma shunts. Methods The 10 and 12 o'clock meridians are marked with a marking pen to define the borders of the conjunctival peritomy. A limbal traction 6-0 Vicryl suture is placed superotemporally in the cornea at the limbus. The conjunctival peritomy is then completed using Westcott scissors along the predetermined marks. The peritomy is extended posteriorly with blunt dissection using Stevens tenotomy scissors. Wet field cautery is used to achieve hemostasis of the scleral bed. A Stevens tenotomy hook is used to identify the superior rectus muscle and a marking pen is used to mark its border. The Ahmed Model FP7 tube shunt is then introduced onto the surgical field. Balanced salt solution is injected into the tip of the tube using a 30-gauge cannula to ensure adequate patency of the valve. The Ahmed plate is then sutured to the sclera approximately 8 mm posterior to the limbus using 5-0 Nylon suture. A corneal paracentesis is made at the 8 o'clock position, and viscoelastic is injected to deepen the anterior chamber. A 23-gauge needle attached to the Healon syringe is then used to tunnel from a point 2.0 mm posterior to the limbus into the anterior chamber. The needle tract is anterior and parallel to the plane of the iris and the surgeon must ensure that the tube does not contact the iris or corneal endothelium after insertion. The implant tube is then laid flush with the cornea and shortened with Westcott scissors with an oblique cut, bevel up. Healon is injected as the needle is withdrawn. Non-toothed forceps are then used to insert the tube into the anterior chamber. A single 8-0 Vicryl suture is used to secure the tube to the underlying sclera. A corneal patch graft is cut to fit the site of tube implantation and secured with a single 8-0 Vicryl horizontal cross mattress suture. The conjunctival peritomy is then closed with a running 8-0 Vicryl suture on a BV needle. Anchoring sutures incorporating the conjunctiva and the episclera to firmly secure the corners of the peritomy to the limbus. A 9-0 Nylon suture is used to re-approximate the limbal conjunctiva. At the conclusion of the case, the eye is returned to a neutral position, the traction suture is removed, and satisfactory intraocular pressure is confirmed by palpation. Results No complications arose during the procedure. Postoperatively, the patient had subconjunctival hemorrhage, injection, and mild pain that decreased over the following week. Prednisolone acetate drops were applied six times daily to prevent inflammation and moxifloxacin drops were applied four times daily to prevent infection. At the three-month follow up, the eye was quiet and intraocular pressure was measured to be 9 mmHg. Conclusion Implantation of an Ahmed glaucoma tube shunt is a safe procedure that can effectively treat various subtypes of glaucoma with sub-optimally controlled intraocular pressure despite maximum medical therapy. Joseph W. Fong, MD Jones Eye Institute, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA JFong@uams.edu Ahmed A. Sallam, MD, PhD Jones Eye Institute, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA ASallam@uams.edu Surgery was performed at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, USA.
Endoscopic Frontal Sinusotomy with Osteoma Removal
videoA 49-year-old female presented with a one-year history of right frontal headaches, not controlled despite OTC medication. Work up with head CT revealed an osteoma of the right frontal sinus. The patient experienced no improvement in headache severity and elected to have surgical intervention. Methods: ENT Fusion Navigation system was used during the entire case. A ball-tip probe was used to fracture out the uncinate bone and a backbiter was used to remove the uncinate in its entirety. The natural ostium of the right maxillary sinus was then visualized. Again, the backbiter was used to remove tissue anterior to the natural ostium. A straight Tru-Cut was used to remove the ostium towards the posterior fontanelle. The right middle turbinate was resected in order to gain sufficient access for the resection of the osteoma. In order to remove the right middle turbinate, a turbinate scissors were used to make 3 cuts along the attachment of the middle turbinate and this was pulled down. A down biter was used to open up the maxillary sinus inferiorly. There was no tissue seen in the maxillary sinus. After this was done, an ethmoidectomy was performed by placing a J-curette behind the ethmoid bulla point anteriorly. This ethmoid bulla was removed along with several other anterior ethmoid cells. After this was done, a frontal sinus seeker was used to identify the right frontal osteoma. The patient did not have a right frontal sinus. Instead, an osteoma was in the area of what would have been the right frontal sinus or nasal frontal outflow tract. Image guidance was meticulously used to identify the osteoma. A 70-degree frontal drill was used and this osteoma was slowly drilled to remove as much as possible. Drilling was done from the posterior edge of the osteoma up to the skull base superiorly, to the lamina papyracea laterally and all bone that could be safely removed was removed. A right frontal propel stent was placed in the bony cavity created by the drill out and after this, the sinus was irrigated and suctioned. Results: The patient was sent to recovery in good condition and no adverse reactions were reported by the surgeon or patient. Surgeons: Alissa Kanaan, MD. Zachary V. Anderson, MD. Institution: Department of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences.
Tongue Reduction (Partial Glossectomy) for Pediatric Macroglossia
videoThis video demonstrates how to perform a tongue reduction using a Y-V advancement technique for pediatric macroglossia.
Pre-operative marking for the Fisher technique in unilateral cleft lip repair
videoThis video outlines the steps taken for pre-operative markings that need to be made prior to performing unilateral cleft lip repair using the Fisher anatomic subunit approximation technique. The technique has been written about in detail by Dr. David Fisher in his article "Unilateral Cleft Lip Repair: An Anatomical Subunit Approximation Technique". This video simply outlines the markings that are made prior to performing this technique, which are crucial for correctly carrying out the repair.
Partial Penectomy due to Penile Calciphylaxis
videoPartial penectomy is the surgical standard of care for invasive tumors of the mid to distal penis, but is utilized in cases of distal penile calciphylaxis due to pain. Partial Penectomy is advantageous compared to a total penectomy, as the patient is able to urinate in the standing position. A 51-year-old man on dialysis for end stage renal disease presented to the emergency department with pain that was increasing in severity for over a month at the glans of the penis. On examination, the glans of the penis was firm with gangrenous necrosis extending distal to the corona, and the urethral meatus was not identified due to the extensive scarring. A clinical diagnosis of penile calciphylaxis was determined and a Partial Penectomy was subsequently performed. Calciphylaxis is a rare life-threatening systemic disease in patients with end stage renal disease due to medial calcification and fibrosis of blood vessels leading to infection and gangrene. The prognosis for penile calciphylaxis tends to be poor with an overall mortality of 64% with a mean time to death of 2.5 months.
Temporal Artery Biopsy
videoTemporal Artery Biopsy - gold standard for the diagnosis of temporal (giant cell) arteritis
Flash Pulse Dye Laser (595nm) Therapy on Facial Capillary Malformation
videoThis video teaches its viewers about facial capillary malformations, possible sequelae, as well as a treatment option, flash pulse dye laser. Authors: Maya Merriweather, BS and Richter T. Gresham, MD FACS Email: mmerriweather@uams.edu and GTRichter@uams.edu Institutions: University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences and Arkansas Children's Hospital
Non-fenestrated Extracardiac Fontan
videoThis video demonstrates a non-fenestrated extracardiac fontan. This is the final step in palliation of hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Authors: Ethan Chernivec; Chris Eisenring, ACNP-BC; Lawrence Greiten, MD; Brian Reemtsen, MD. Arkansas Children's Hospital, Department of Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery, Little Rock, AR University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences College of Medicine, Little Rock, AR
Closure of a Large Secundum ASD
videoInstitution: University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Authors: Thomas Heye - teheye@uams.edu Lawrence Greiten MD - lgreiten@uams.edu Christian Eisenring ACNP-BC - EisenringC@archildrens.org
Transannual Patch Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot
videoInstitution: University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Authors: Thomas Heye - teheye@uams.edu Lawrence Greiten MD - lgreiten@uams.edu Christian Eisenring ACNP-BC -EisenringC@archildrens.org
RV-PA Conduit Replacement in d-TGA
videoReplacement of a stenotic/irregular right ventricle to pulmonary artery Gore-Tex trileaflet graft with a novel KONECT RESILIA Aortic Valved Conduit. This is the only tissue valved conduit currently in use. This patient has d-transposition of the great arteries along with ASD, VSD, pulmonary stenosis, bovine left arch and aberrant right subclavian arteries. His previous operations include MBTS 4mm Gore-Tex graft, urgent shunt revision secondary to thrombosis and subsequent conversion to a 4mm central shunt, right atrial thrombectomy secondary to indwelling right atrial catheter, takedown of central shunt, primary pledgeted closure of pulmonary valve, Gore-Tex patch closure of ASD/VSD, Rastelli procedure with 24mm Gore-Tex trileaflet with bulging sinuses graft.
Aortic Valve Replacement via the Ross Procedure
videoA brief patient history is provided, followed by preoperative imaging, intraoperative repair, and postoperative imaging.
Medial Orbital Dermoid Cyst Removal
videoDermoid cysts are the most common orbital tumor in childhood. It is a developmental benign choristoma, arising from ectodermal sequestration along the lines of embryonic fusion of mesodermal processes. It is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium and expands slowly due to constant desquamation and dermal glandular elements. They are usually smooth, painless, mobile, or partially mobile lesions mostly present at the fronto-zygomatic suture with proptosis, displacement, ptosis, or diplopia, depending on depth and extent1. Although lateral orbital dermoid cysts are common, medial orbital dermoid cysts are rare2. Our patient had a right medial orbital congenital dermoid cyst since birth. At the presentation, the patient was 2 years old. On CT, the cyst measured 5 mm at the upper lid/medial canthus of the right orbit with subtle bone remodeling. He had a mildly clogged tear duct on the left but was otherwise asymptomatic. The decision was made to surgically remove the dermoid cyst. In this video, we present a case of removal of a medial orbital dermoid cyst in a 2-year-old patient. An incision was planned directly over the lesion. It was marked following the natural skin tension lines of the face to give the most natural esthetic appearance. A small amount of Local anesthetic (0.5 ml of Lidocaine and Epinephrine) was injected under the skin to promote hemostasis and postoperative pain control. A continuous Incision was made with a #15 blade on the skin. Westcott scissors were used to dissect further through the subcutaneous tissue to expose the cyst and slowly dissect it from the normal tissue surrounding it. Extra care was made to protect the integrity and avoid the rupture of the cyst. After the entire cyst was freed from the surrounding tissue, it was carefully removed from its attachments to the periosteum using Westcott scissors. The incision was closed in a two-layer fashion. The deeper layer was closed by 6.0 Vicryl in a vertical mattress fashion with 2 interrupted sutures. Next, wound edge eversion was achieved by placing two interrupted, superficial 5.0 fast-absorbing gut sutures. This will minimize the scar appearance. Dermabond was applied next and the sutures were protected by a small piece of Tegaderm. This will be left in place until it spontaneously falls off.
Nasal Dermoid Cyst Excision
videoThis is a case of an 8 month old with a midline nasal mass present since birth. Preoperative physical exam and imaging was consistent with a nasal dermoid cyst with no evidence of intracranial extension.
A Pediatric Case of Levator Palpebrae Resection
videoIn this video, we present a case of levator palpebrae resection in an 8-year-old patient with right eye ptosis. In the pre-op photo, significant ptosis of the right eye can be appreciated. An incision was planned along the lid crease. 0.1 ml of 1: 100,000 epinephrine was injected. An incision was made by electro-cautery along the lid through the skin and orbicularis. Westcott scissors were used to further dissect horizontally. The septum was identified and opened. The preaponeurotic fat was identified and lifted, and the levator aponeurosis was identified. The levator was then tagged with two 6.0 Vicryle sutures, and isolated from surrounding tissues. Next, three6-0 Mersilene sutures were run from the upper tarsus to the levator. They are tightened with releasable notes. The lid elevation and contour were evaluated and adjustments were made until contour and height were equal and appropriate. The temporary surgical knots were transitioned into permanent surgical knots. Approximately 14 mm of excess levator was then excised. Next, three lid crease formation sutures were placed using 6-0 Vicryl. These were attached to the subcu-skin and levator to recreate the upper eyelid crease. Skin closure was performed with 6-0 fast-absorbing gut sutures. In this one-week post-op photo, the ptosis of his right eye was improved. Thank you for watching!
Tetralogy of Fallot Repair
videoComplete repair of Tetralogy of Fallot with a transannular patch. The patient is placed on cardiopulmonary bypass in the standard fashion. An incision in made into the free wall of the right ventricle and the septal defect is exposed. A non-autologous CorMatrix patch is placed with prolene suture in a running fashion to repair the septal defect. An additional patch is used to repair the right ventricular outflow tract with a similar running suture. The patient was removed from cardiopulmonary bypass and extubated in the operating room.
Laryngeal Papillomatosis with Microlaryngoscopy and Bronchoscopy with Microdebridement, CO2 Laser Ablation, and Cidofovir Injections.
videoAnna Celeste Gibson, B.S., Mariah Small, M.D., Gresham Richter, M.D. University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Arkansas Children's Hospital Introduction: A papilloma is a benign tumor that is caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) commonly due to the strains 6 and 11. Children acquire these tumors intrapartum from an infected mother. HPV infects natural and metaplastic squamous mucosa which is the type of epithelium that lines the vocal folds. Tumors present as numerous, verrucous outgrowths from the mucosa and can become symptomatic due to mass effect. Common symptoms include hoarseness, dysphonia, aphonia and most concerning, respiratory distress. A 7-year-old patient with dysphonia secondary to laryngeal papillomatosis also known as recurrent respiratory papillomatosis undergoes microlaryngoscopy and bronchoscopy with microdebridement, CO2 laser ablation, and cidofovir injections. Methods: The patient underwent spontaneous ventilation anesthesia and a dental guard was placed. The patient was positioned for microlaryngoscopy and the larynx was visualized and anesthetized with topical lidocaine. A zero-degree Hopkins rods was passed through the supraglottis, glottis and subglottis to document findings. There was supraglottic papillomatosis notably of the laryngeal surface of the left epiglottis, papillomatosis of the bilateral false vocal folds and papillomatosis of the bilateral true vocal folds with right more affected than left and anterior commissure involvement. The scope was then withdrawn and reintroduced to perform bronchoscopy. The scope was advanced through the trachea, carina and primary and secondary bronchi bilaterally. All were within normal limits. The Benjamin-Lindholm laryngoscope was passed into the vallecula and larynx and suspended in a normal fashion. The zero-degree Hopkins rod was used to visualize the larynx. 2 cc of 1% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine was injected into the bulk of the papillomas and then several biopsies were taken from this area. The microdebrider was used to debulk these areas. Protective eyewear was used by everyone in the operating room. The patient's face was protected with water soaked towels and all oxygen sources were removed from the patient. The CO2 laser was set to 2 watts continuous and used to debulk the papillomas with eschar noted after each application. Care was taken to avoid injury to the deep elements of the true vocal folds. Any residual papillomas at the anterior vocal folds were then injected with 1 cc of cidofovir. All instrumentation was removed, the patient was extubated, awakened, and transferred to the recovery room. Results: The patient was discharged the same day without complications. He will follow up for revision microdebridement, CO2 laser ablation and cidofovir injections. Conclusion: Microlaryngoscopy and bronchoscopy with microdebridement, CO2 laser ablation, and cidofovir injections is a successful solution for laryngeal papillomatosis and has been proven to eradicate the disease in many cases.
Branchial Cleft Cyst Excision
videoBranchial cleft cysts are a benign anomaly caused by incomplete obliteration of a primordial branchial cleft. They typically appear in childhood or adolescence, but can appear at any age. They present as a non-tender, fluctuant mass following an upper respiratory infection, most commonly at the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. These lesions are thought to originate during the 4th week of gestation when the branchial arches fail to fuse. The second branchial cleft is the most common site (95%) and cysts from in this distribution can affect cranial nerves VII, IX, and XII.
Pediatric Lumbar Epidural Catheter Placement via the Landmark Technique.
videoThis video demonstrates an epidural catheter placement on a 2-year-old, 12kg male patient presenting for left hip osteotomy. His past medical history was remarkable for congenital heart defects, bilateral congenital hip dislocations, and a sacral dimple which is sometimes associated with neurologic spinal canal abnormalities. In this case, no neurologic anatomical abnormalities were demonstrated on the neonatal spine ultrasound. The patient was placed in a left lateral decubitus position. Using anatomical landmarks like Tuffier’s line or the intercristal line corresponding to L4-L5 level, the target level for needle placement was identified and marked. The patient’s skin was sterilized and draped under sterile conditions. An 18-gauge, 5 cm length Tuohy needle was used to encounter the epidural space. A general guideline for the depth to the epidural space from the skin is approximately 1mm/kg of body weight¹. Subsequently, a 20-gauge catheter was placed through the needle to a depth of 4.5 cm at the level of the skin. Negative aspiration of blood or CSF was confirmed. A test dose was calculated at 0.5 mcg/kg epinephrine or 0.1ml/kg of lidocaine 1.5% with epinephrine 1:200,000. In this case, a 1.2 mL test dose of lidocaine 1.5% with epinephrine 1:200,000 was given without any observed cardiovascular changes (e.g. ≥ 25% increase or decrease in T wave amplitude, HR increase ≥ 10 bpm, or SBP increase ≥ 15 mmHg)¹. Finally, the catheter was secured to the back of the patient. Parental consent was obtained for the publication of this video.
Jump Graft Repair of Coarctation of the Aorta
videoThis is a video showcasing a jump-graft repair for Coarctation of the aorta.
Coarctation of the aorta is one of the most well-known and documented congenital heart defects. Innovations in the field have led to a several options for surgical repair. However, patients with coarctation of the aorta remain at high risk for a number of morbidities including recoarctation aortic aneurysms and dilations, and sudden death. Our video showcases a jump graft repair, which is an underutilized approach for coarctation repair. Our goal is to educate others in the field on the proper technique and utility of this operation.
Thyroid Cyst Removal with Hemithyroidectomy
videoThis video shows a thyroid cyst removal that resulted in a hemithyroidectomy. The patient is placed under general anesthesia and intubated using a mac video laryngoscope and an EMG endotracheal tube. The ET tube has 4 stainless steel wire electrodes which touch the vocal cords for monitoring during surgery. After video intubation electrode placement is verified by direct stimulation of the area. The surgeon makes a curvilinear skin crease incision in the front of the neck, to minimize the visibility of a scar. Afterwards, subplatysmal flaps are elevated and the midline raphe is dissected exposing the sternohyoid muscle, which is retracted laterally, and the sternothyroid muscle that is dissected off the left thyroid gland. The thyroid cyst is found superficial and dissected, keeping in mind that anything suspicious for the recurrent laryngeal nerve is stimulated prior to dissection. The cyst is ruptured and sent for frozen pathology. The results returned as thyroid, so the surgeon proceeded with a hemithyroidectomy. The superior and inferior parathyroids were identified and dissected free. Hemostasis was achieved with electrocautery and confirmed with Valsalva. Strap musculature platysma and skin are closed. And lastly, mastisol and steri-strips are placed perpendicular to the wound.
Excision of a Dermoid Cyst
videoThis video demonstrates the excision of a supraorbital dermoid cyst in a pediatric patient. This lesion was located just superior to the right lateral orbit.
Excision of greater occipital nerves and 3rd occipital nerves
videoAbstract Introduction: Occipital headache is a common, costly and debilitating disease process.When traditional therapies such as medication management and physical therapy fail to provide relief, surgical interventions may be considered. This procedure involves the excision of the 3rd and both greater occipital nerves. Case presentation: 36 years old. female with history of chronic refractory occipital headaches involving both greater occipital nerves and 3rd occipital nerves who presented for resection of those nerves. Methods: A 10cm incision was marked on the posterior neck, positioned inferior to the occipital skull base. Subsequently, the incision was carefully extended through the subcutaneous tissue. By means of both blunt and sharp dissection through the posterior muscle fascia where it inserts into the skull base, the right greater occipital nerve was identified and dissected into the paravertebral muscles and several centimeter of the nerve was resected so it could not grow back together. A corresponding procedure was employed for the left greater occipital nerve, located approximately 3 cm from the midline, and excised using the same technique. Additionally, the third occipital nerves situated in the midline were excised to address the entirety of the issue. Following these procedures, the wound was thoroughly irrigated with normal saline to ensure cleanliness, and hemostasis was diligently maintained throughout the surgical intervention using both monopolar and bipolar cautery. To alleviate postoperative discomfort, 0.5% Marcaine with epinephrine was carefully injected into the nerve areas. The fascia needs to be closed with strong sutures and the skin and subcutaneous tissue were closed in two layers. Conclusion :The excision of greater occipital nerves presents a viable option for the management of chronic occipital headaches when conservative treatments prove ineffective. This case report highlights the successful outcome of such a procedure in a 36-year-old female suffering from debilitating headaches Surgeons: Dang-Khoa Nguyen, MD James Y Suen,MD Conflicts of Interest: None Funding: This research received no external funding Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, USA
Excision of supratrochlear and supraorbital nerves
videoAbstract Introduction: Frontal headache is a common, costly and debilitating disease process.When treatments, including medication management and physical therapy, prove ineffective, surgical interventions become a viable consideration Among these interventions, the excision of supratrochlear and supraorbital nerves stands out as a potential therapeutic option. Case presentation: 24-year-old female with history of chronic frontal headaches who presents for resection of supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves. Methods: A 4 cm incision was carefully made along the right eyebrow. This incision extended through the subcutaneous tissue. Employing a combination of blunt and sharp dissection techniques, we successfully identified supratrochlear nerves, observing multiple branches emerging from the orbit. All branches were excised via scissors . Subsequently, we located the supraorbital nerve exiting through a foramen, just above the mid-orbital rim, and proceeded to excise it. The wound was thoroughly irrigated with normal saline to ensure cleanliness, and hemostasis was maintained throughout the procedure using both monopolar and bipolar cautery. Closure of the incision was executed in a layered fashion, employing 3-0 Monocryl and 5-0 Chromic sutures. To minimize postoperative discomfort, 0.5% Marcaine with epinephrine was injected into the nerve areas. Conclusion :The excision of the supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves offers a promising option for managing chronic frontal headaches when conventional treatments prove ineffective. This case report underscores the successful outcome of this procedure in a 24-year-old female who had been enduring debilitating headaches. Surgeons: Dang-Khoa Nguyen, MD James Y Suen,MD Conflicts of Interest: None Funding: This research received no external funding Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, USA
Epicardial Lead Extraction after Sudden Cardiac Arrest
videoInstitution: University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Authors: Monroe McKay mpmckay@uams.edu Ashley Wilson Christian Eisenring Brian Reemtsen Lawrence Greiten
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) Resection
videoAbstract Introduction: Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are abnormal connections between arteries and veins that lack an intervening capillary network. The high flow of arterial blood directly into veins can lead to the weakening of venous walls, potentially resulting in life-threatening hemorrhages.The primary treatment modalities for cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) include surgical resection, endovascular embolization. Case presentation: A 34-year-old female presented with a roughly 7x7 cm arteriovenous malformation (AVM) located in the right temporoparietal area. The AVM extended both superficially and deeply into the infratemporal fossa and laterally towards the orbit. Imaging revealed the presence of multiple large contributing vessels in the preauricular area. The patient underwent embolization with interventional radiology one day prior to the surgical procedure. Methods: Markings were made along the right upper hairline after trimming and continued down the preauricular skin. A #15 blade was utilized to make incisions through the epidermis and dermis, reaching the subcutaneous tissues. The temporoparietal and temporal flap fascia were dissected and carefully raised. Once the AVM was detached from the surrounding temporalis muscle and the zygomatic bone, its feeder vessels were ligated near the tragal pointer using hemoclips to aid in future localization. Hemostasis was successfully achieved with bipolar cautery. The temporalis muscle and its adjacent fascia were sutured closed with vicryl suture. Closure of the deep dermal layer was accomplished with 4-0 PDS, and the skin was closed in a running subcutaneous fashion using 5-0 monocryl. Conclusion : We present a successful surgical resection of Arteriovenous Malformation with a prior embolization by interventional radiologist Surgeons: Coleman, Madison, MD, Aryan D Shay ,MD Gresham T Richter, MD, FACS Conflicts of Interest: None Funding: This research received no external funding Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, USA Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, AR, USA
Eagle Syndrome (Calcification of the Stylohyoid Ligament) Excision
videoAbstract Introduction: Eagle syndrome can affect many patients of any age, anywhere from 25 to 80 years old. The most common symptoms are ear and anterior superior neck pain underneath the angle of the jaw, tinnitus, some throat symptoms, and dizziness. There are two approaches that can be done for surgery, with our preference being for the intraoral approach. The pathophysiology is that the stylohyoid ligament becomes calcified and can cause pressure on blood vessels and nerves, causing variable symptoms. It is frequently undiagnosed causing patients to visit several physicians before correctly identifying the problem. A CT scan of the neck with or without contrast, can help identify the problem. Case presentation: A 39-year-old female with a history of ear and upper neck pain at the angle of the jaw. CT imaging showed calcification of the stylohyoid ligament. Surgery was recommended and a trans-oral approach was used. Methods: General anesthesia with muscle relaxation was used. A crow Davis or Dingman tractor was used to retract the endotracheal tube to allow exposure of the Oropharynx. Betadine was used to help sterilize the oropharynx. Palpation on each side is done to localize the calcified ligament and if present, the surgery is much easier to do. A 2.5 cm vertical incision is made in the anterior tonsillar pillar, being careful not to go too high on the soft palate because it can paralyze the soft palate causing significant reflux into the nasopharynx and nose, with speech and swallowing problems. The tonsil capsule and the medial pterygoid muscle are identified, and the dissection is between the two. The calcified ligament is usually about 2.5 cm deep to that area. It is in or under the fat pad in the prevertebral area. It may be difficult to find, and it is helpful if your finger is passed through the incision to palpate deeper to feel the bony process. The stylohyoid muscle and fat must be cleaned off the bone as high and low as can be dissected ideally using a combination of the monopolar and bipolar cautery. It is important to be careful in this area with the monopolar cautery because of the proximity to the internal carotid artery and jugular vein. Also, the vagus nerve can be injured. A Kerrison rongeur is used to fracture the bone superiorly. The ligament is connected at the inferior part which can be divided with the cautery. It is important to obtain good hemostasis using the bipolar cautery and saline irrigation. The wound is closed by sewing the tonsil capsule to the medial pterygoid muscle after which the mucosal incision is sewed. Preferably, vicryl sutures are used so that it will last approximately four weeks. Bupivacaine 0.5% can be injected around the surgical site to decrease postop pain. The surgery is done as an outpatient basis and the patient is given pain medication and antibiotics for significant throat pain lasting 7 to 10 days postop. Conclusion: The removal of the calcified Stylohyoid ligament via an intraoral approach, can be simple or very complicated, and must be done carefully by an experienced surgeon to avoid major complications. Most patients benefit significantly with relief of their symptoms and are very grateful. This case illustrates the surgical procedure that was easy to perform, but they are not all that easy. Surgeons: Siddharth Patel, MD James Y Suen, MD Conflicts of Interest: None Funding: This research received no external funding Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, USA
leadership (2)
Michael Golinko, MD
leadership
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
- Medical Director of Craniofacial Program, Arkansas Children’s Hospital
- Assistant Professor of Plastic Surgery, UAMS
Dr. Michael Golinko, M.D., is a Board Certified General Surgeon with clinical interests in Craniofacial, Cleft & Paediatric Plastic Surgery. Dr. Golinko is also Board Eligible with the American Board of Plastic Surgery, and is licensed in the states of Arkansas, and Georgia. Currently, Dr. Golinko serves as one of the Medical Directors of Arkansas Children’s Hospital Craniofacial Program, and is Assistant Professor of Plastic Surgery at the University of Arkansas Medical Sciences.
Dr. Golinko received his M.D. degree from University of South Florida (USF) in 2004, preceded by a M.A. in Medical Anthropology from Universiteit van Amsterdam (UVA) in 2002, and a B.Sc. in Physics from Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1998.
Dr. Golinko’s professional training includes General Surgery residencies at State University of New York (SUNY) and New York University (NYU), as well as a residency in Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery at Emory University School of Medicine, and he most recently served as a Fellow in Craniofacial Surgery/Pediatric Plastic Surgery at New York University (NYU).
From 1998 to 2008, Dr. Golinko held medical research positions at MIT, Massachusetts General Hospital, and completed Post-Doctoral Research Fellowships in the Department of Surgery, Division of Wound Healing at both Columbia University and New York University.
Dr. Golinko has contributed extensively to numerous peer-reviewed publications, book chapters, and abstracts. Moreover, Dr. Golinko has travelled the world to deliver numerous presentations, co-chair lectures and conferences, and media appearances.
Dr. Golinko has been awarded and recognized for the following: Operation Smile Regan Fellowship Recipient (2012), National Institute of Health (NIH) Loan Repayment Program Recipient (2007 – 2009), and Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons, Department of Surgery, Startup Grant (2006).
In the spirit of a true leader, Dr. Golinko served as past-President and Mission Leader of Project World Health, Managing Trustee of the Barry Golinko Trust of the Jewish Communal Fund, past-Surgery Department Representative of the Committee on Interns and Residents (CIR) and currently was selected to participate in the Arkansas Children’s Hospital Physician Leadership Development course.
Dr. Golinko currently belongs to several professional societies as follows: American Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Association, American Association of Wound Care, American College of Surgeons, and the Southeastern Society Of Reconstructive Plastic Surgeons.
In 2016, Dr. Golinko served on the American Society of Maxillofacial Surgeons/Plastic Surgery Foundation Combined Pilot Research Grant Committee. In addition to his professional work, Dr. Golinko has generously donated his time and many talents to numerous volunteer and humanitarian efforts all over the world.
Destiny F. Chau, MD, FAAP
leadership
Professor of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine / Pediatric Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology
Arkansas Children's Hospital / University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Dr. Destiny F. Chau is a board-certified anesthesiologist and pediatric anesthesiologist. She is currently a Professor of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. After graduating with the highest honors with an undergraduate degree in chemical engineering, Dr. Chau earned her medical degree from the University of Kentucky College of Medicine in 2002. She finished anesthesiology residency training in 2006 at this institution and later completed a pediatric cardiac anesthesiology fellowship at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. Since then, she has dedicated her professional time to advancing clinical medicine and medical education at national and international levels. Dr. Chau regularly participates in short-term medical and surgical initiatives in low- and middle-resourced areas with a focus on service and education. Dr. Chau held several leadership positions at the University of Kentucky College of Medicine and Eastern Virginia Medical School prior to joining the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences as a Fellowship Program Director in 2020.
management (1)
Deanne King, M.D., Ph.D.
management
- Assistant Professor, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
- Director of Clinical Research, Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
King has a Bachelor of Science in biochemistry from the Texas A&M University in College Station. She has an M.D./Ph.D. in molecular and cellular biology and pathobiology from the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston. She completed an internship in general surgery and a surgery residency in otolaryngology-head and neck surgery, both at UAMS.
King said she enjoys helping researchers make connections.
“Research can sometimes be an isolating pursuit, but collaboration and idea-sharing is so important to the overall process,” King said. “I’m also looking forward to helping our students and residents. Otolaryngology-head and neck surgery is a highly competitive field. Having published research to your name early in your career is not only a valuable experience, but, increasingly, a necessity for medical students to successfully match into an otolaryngology residency.”
Faculty in the Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery are fellowship-trained in their specialty and cover all the sub-specialties in the field (otology, endocrine, head and neck, rhinology, laryngology, pediatric and vascular anomalies). The faculty consistently receive high scores on patient satisfaction, and six faculty are listed in “Best Doctors in America.” They practice at UAMS Medical Center, Arkansas Children’s Hospital and the Central Arkansas Veterans Health Care System.
webinar (8)
Surgical Pitfalls, Early Career Advancement and Leadership
webinar
In this last Cardiothoracic DocTalk session of the Pathway to Independence for Junior Surgeons we will discuss early career mistakes and how to avoid them. Viewers of this webinar will learn tips and tricks learned from senior partners and knowing when to call for help.

Lawrence Greiten, MD
Assistant Professor in Division of Congenital Cardiac Surgery
Arkansas Children's Hospital (ACH) and the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS)
Lawrence Greiten, M.D., is an Assistant Professor in the Division of Congenital Cardiac Surgery at Arkansas Children’s Hospital (ACH) and the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS). Dr. Greiten received his undergraduate degree from Kansas Wesleyan University and his medical degree from the University Of Arizona College Of Medicine. He completed both his General Surgery training and Cardiovascular and General Thoracic Surgery fellowship at the Mayo School of Graduate Medical Education, where he also earned a Masters in Biomedical Sciences, Clinical and Translational Science. He did an advanced Fellowship in Congenital Cardiac Surgery at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, Keck Medical School at the University of Southern California.
Surgical Exposure, Minimal Incision Surgical Option for ASD Repair
webinar
In this second Cardiothoracic DocTalk session of the Pathway to Independence for Junior Surgeons we plan to discuss the approach to a Minimal Incision ASD. Our panel will discuss the merits of offering this approach along with the potential pitfalls. Viewers of this webinar will gain insight into optimizing surgical exposure and understanding when it is safe to proceed with less invasive techniques.

Lawrence Greiten, MD
Assistant Professor in Division of Congenital Cardiac Surgery
Arkansas Children's Hospital (ACH) and the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS)
Lawrence Greiten, M.D., is an Assistant Professor in the Division of Congenital Cardiac Surgery at Arkansas Children’s Hospital (ACH) and the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS). Dr. Greiten received his undergraduate degree from Kansas Wesleyan University and his medical degree from the University Of Arizona College Of Medicine. He completed both his General Surgery training and Cardiovascular and General Thoracic Surgery fellowship at the Mayo School of Graduate Medical Education, where he also earned a Masters in Biomedical Sciences, Clinical and Translational Science. He did an advanced Fellowship in Congenital Cardiac Surgery at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, Keck Medical School at the University of Southern California.
Pre-Operative Planning, Intraoperative Considerations and Troubleshooting
webinar
In this first Cardiothoracic DocTalk session of the Pathway to Independence for Junior Surgeons we will discuss Redo Sternotomy and Pulmonary Valve Replacement in a patient who had prior TOF repair. We plan to highlight the pre-operative strategy which will include necessary imaging and testing along with how to manage an intra-operative complication of air embolism. Viewers of this webinar will gain valuable insight into a stepwise approach to managing a very complex surgical scenario.

Lawrence Greiten, MD
Assistant Professor in Division of Congenital Cardiac Surgery
Arkansas Children's Hospital (ACH) and the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS)
Lawrence Greiten, M.D., is an Assistant Professor in the Division of Congenital Cardiac Surgery at Arkansas Children’s Hospital (ACH) and the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS). Dr. Greiten received his undergraduate degree from Kansas Wesleyan University and his medical degree from the University Of Arizona College Of Medicine. He completed both his General Surgery training and Cardiovascular and General Thoracic Surgery fellowship at the Mayo School of Graduate Medical Education, where he also earned a Masters in Biomedical Sciences, Clinical and Translational Science. He did an advanced Fellowship in Congenital Cardiac Surgery at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, Keck Medical School at the University of Southern California.
Alveolar Bone Graft Surgery: Tips and Tricks
webinar
This webinar will focus on the surgical management of alveolar clefts with bone grafting and fistula closure. Our panel of experts will share various techniques and graft source materials including tips and tricks learned along the way. Our guest moderator will lead a panel discussion at the end of the session to discuss some of the controversies and key points in alveolar grafting.






| Dr. Larry Hartzell Director of Cleft Lip and Palate / Pediatric ENT Surgeon @ Arkansas Children's Hospital / University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences | Dr. Steven Goudy Professor / Director of Division of Otolaryngology @ Emory University School of Medicine / Children's Healthcare in Atlanta |
|---|---|
| Larry Hartzell, MD FAAP is an Associate Professor of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery at Arkansas Children’s Hospital. He is the Director of the Pediatric Otolaryngology fellowship. Dr Hartzell also has been the Cleft Team Director in Arkansas since 2012. He is passionate about international humanitarian mission work and dedicates much of his research efforts to cleft surgical and clinical care as well as velopharyngeal insufficiency. Dr Hartzell is actively involved in multiple academic societies and organizations including the AAO-HNS and ACPA. | Dr. Goudy is a professor at Emory University School of Medicine and the director of the division of otolaryngology at Children’s Healthcare in Atlanta. Dr. Goudy’s clinical job involves repair of craniofacial malformations including cleft lip, cleft palate, and Pierre Robin sequence, and he also participates in head and neck tumor resection and reconstruction. |
| Travis T. Tollefson MD MPH FACS Professor & Director of Facial Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery @ University of California Davis | Mark E. Engelstad DDS, MD, MHI Associate Professor of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery @ Oregon Health & Science University |
|---|---|
| Dr. Tollefson is a Professor and Director of Facial Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery at the University of California Davis, where he specializes in cleft and pediatric craniofacial care, facial reconstruction and facial trauma care. His interest in the emerging field of Global Surgery and improving surgical access in low-resource countries led him to complete an MPH at the Harvard School of Public Health. He helps lead the CMF arm of the AO-Alliance.org, whose goal is to instill AO principles in facial injuries in low resource settings. His current research focuses on clinical outcomes of patients with cleft lip-palate, facial trauma education in Africa, patterns of mandible fracture care, and patient reported outcomes in facial paralysis surgeries. He serves on the Board of Directors of the American Board of Otolaryngology- Head and Neck Surgery, American Academy of Facial Plastic Surgery, and is the Editor-In-Chief for Facial Plastic Surgery and Aesthetic Medicine journal. | Mark Engelstad is Associate Professor and Program Director of Oral and Maxillofacial surgery at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, Oregon. His clinical practice focuses on the correction of craniofacial skeletal abnormalities, especially orthognathic surgery and alveolar bone grafting. |
| John K. Jones, MD, DMD Associate Professor in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery @ University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences / Arkansas Children’ Hospital | David Joey Chang, DMD, FACS Associate Professor of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery @ Tufts University/Tufts Medical Center |
|---|---|
| Dr. Jones has over 30 years of experience in the surgical management of cleft lip and palate with particular experience in the area of alveolar ridge grafting and corrective jaw surgery. He has been a member of the Cleft Lip and Palate Team at Arkansas Children’s Hospital for the last six years. During that time he has worked with Dr. Hartzell and his team to introduce and innovate new techniques, many from the realm of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Dentistry, in the interest of improving outcomes for this most challenging patient population. | Dr. Chang is an associate professor at Tufts University School of Medicine and Tufts Medical Center. Dr. Chang is involved in the Cleft Team at Tufts Medical center since 2012. He also focuses on advanced bone grafting procedures, TMJ surgery, and nerve reconstruction. |
Three Stage Management of the Single Ventricle
webinar
In this session our team of experts will discuss the three stages of single ventricle palliation including the Norwood procedure, the bidirectional Glenn shunt and the Fontan procedure. Included in this webinar will be single ventricle pathophysiology, diagnostic studies/imaging, indications and contraindications for palliation, timing of surgical intervention, and overview of surgical goals and associated mortality.


Assistant Professor in Division of Congenital Cardiac Surgery
Arkansas Children's Hospital (ACH) and the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS)
Lawrence Greiten, M.D., is an Assistant Professor in the Division of Congenital Cardiac Surgery at Arkansas Children’s Hospital (ACH) and the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS). Dr. Greiten received his undergraduate degree from Kansas Wesleyan University and his medical degree from the University Of Arizona College Of Medicine. He completed both his General Surgery training and Cardiovascular and General Thoracic Surgery fellowship at the Mayo School of Graduate Medical Education, where he also earned a Masters in Biomedical Sciences, Clinical and Translational Science. He did an advanced Fellowship in Congenital Cardiac Surgery at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, Keck Medical School at the University of Southern California.
Research Intern
Arkansas Children’s Research Institution / University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Sophia is a Pre-Medical Track student that recently graduated with a traditional BA-Biology degree and a minor in Medical Humanities. She is always seeking to expand her knowledge and gain exposure to pediatric research in hopes of bettering herself as an aspiring physician and continuing research in the future.


CVOR Surgical Assistant Chief
Arkansas Children's Hospital
Over 28 years of adult and congenital heart surgery experience. I have helped develop a minimally invasive and robotic surgery program at UCLA. In addition, I have been involved with Ex-Vivo heart and lung preservation trials and several drug trials.
Professor, Department of Surgery / Director, Heart Institute
UAMS College of Medicine / Arkansas Children’s Hospital
Brian Reemtsen, M.D. is a Professor at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in the Division of Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery at Arkansas Children’s Hospital. He is also Director of the Heart Institute at Arkansas Children’s Hospital. He received his undergraduate degree from the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA), and his medical degree from New York Medical College. He completed his internship and residency at UCLA School of Medicine. He then completed fellowships at the University of Washington, as well as the Great Ormond Street Hospital in London, England.

Pediatric Cardiologist
Arkansas Children's Hospital
After completion of her formal training, Dala Zakaria, M.D., joined the faculty of the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in 2013, practicing at Arkansas Children’s. Her primary clinical interests are transesophageal and fetal echocardiography, and advanced imaging, including 3D. Dr. Zakaria performs and interprets transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiograms in our outpatient, inpatient and telemedicine programs. She is an integral part of the Fetal Echocardiography program, providing fetal echocardiogram interpretation and consultation.
Ventricular Septal Defects
webinar
As one of the most common congenital cardiac anomalies managed by pediatric cardiac teams, VSD’s often may present a challenge in optimal management. Our team of experts will discuss pathophysiology, diagnostic studies, indications and timing of surgery, surgical management; along with the technical challenges/considerations of repairing each of the different anatomic variants of ventricular septal defects: perimembranous, conoventricular, supracristal (subpulmonary), inlet (atrioventricular canal type), and muscular.


Assistant Professor in Division of Congenital Cardiac Surgery
Arkansas Children's Hospital (ACH) and the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS)
Lawrence Greiten, M.D., is an Assistant Professor in the Division of Congenital Cardiac Surgery at Arkansas Children’s Hospital (ACH) and the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS). Dr. Greiten received his undergraduate degree from Kansas Wesleyan University and his medical degree from the University Of Arizona College Of Medicine. He completed both his General Surgery training and Cardiovascular and General Thoracic Surgery fellowship at the Mayo School of Graduate Medical Education, where he also earned a Masters in Biomedical Sciences, Clinical and Translational Science. He did an advanced Fellowship in Congenital Cardiac Surgery at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, Keck Medical School at the University of Southern California.
Research Intern
Arkansas Children’s Research Institution / University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Sophia is a Pre-Medical Track student that recently graduated with a traditional BA-Biology degree and a minor in Medical Humanities. She is always seeking to expand her knowledge and gain exposure to pediatric research in hopes of bettering herself as an aspiring physician and continuing research in the future.


CVOR Surgical Assistant Chief
Arkansas Children's Hospital
Over 28 years of adult and congenital heart surgery experience. I have helped develop a minimally invasive and robotic surgery program at UCLA. In addition, I have been involved with Ex-Vivo heart and lung preservation trials and several drug trials.
Professor, Department of Surgery / Director, Heart Institute
UAMS College of Medicine / Arkansas Children’s Hospital
Brian Reemtsen, M.D. is a Professor at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in the Division of Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery at Arkansas Children’s Hospital. He is also Director of the Heart Institute at Arkansas Children’s Hospital. He received his undergraduate degree from the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA), and his medical degree from New York Medical College. He completed his internship and residency at UCLA School of Medicine. He then completed fellowships at the University of Washington, as well as the Great Ormond Street Hospital in London, England.


Assistant Professor, Pediatric Cardiology & Radiology
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences / Arkansas Children’s Hospital
Dr. Merves is a pediatric cardiologist with a specific interest and additional training in cardiac imaging. In clinical practice, she cares for patients across all age ranges from fetal life through adulthood and performs and interprets fetal echocardiograms, transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiograms, cardiac MRIs and cardiac CTs. She has an interest in imaging related research and education.
Pediatric Cardiologist / Associate Professor of Pediatrics / Pediatric Cardiology Fellowship Program Director
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences / Arkansas Children’s Hospital
Dr. Daily is a non-invasive pediatric cardiologist who serves as the Pediatric Cardiology Fellowship Program Director at Arkansas Children’s Hospital. His interests include echocardiography, adult education, and physician personal finance.
The Ins and Outs of Medical Research & Publication
webinar
The International Journal of Medical Students and CSurgeries have come together to provide and exclusive inside scoop on the world of medical publications. They will review how to properly research and submit an article along with selecting the best journal to publish through.


Editor in Chief
International Journal of Medical Students
Francisco is the Editor in Chief of the IJMS. He is a physician and has a master's in epidemiology from the Universidad del Valle (Colombia). He is currently finishing a PhD in Clinical Research and Translational Science at the University of Pittsburgh. He is also the CEO of the research foundation Science to Serve the Community, SCISCO (Colombia), and is an Assistant Professor at Universidad del Valle in Colombia teaching research to ophthalmology residents.
Francisco is a researcher of several groups in public health, ophthalmology and visual sciences, injuries, mental health, global surgery, and rehabilitation, and he was ranked as an Associate Researcher by the Colombian Ministry of Science, Innovation & Technology."
Pediatric Otolaryngologist / Assistant Professor
Seattle Children's Hospital / University of Washington
Dr. Bonilla-Velez is a pediatric otolaryngologist at Seattle Children's Hospital and an Assistant Professor in the Department of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery at the University of Washington. Originally from Cali, Colombia, Dr. Bonilla-Velez completed her medical school in the Universidad del Valle, Colombia. She then did a postdoctoral research year at Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, after which she started residency at the University of Arkansas for Medical Studies in Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery before coming to Seattle Children’s for fellowship in pediatric otolaryngology. She also serves as a founding editor of the International Journal of Medical Students (IJMS).


Chief of Pediatric Otolaryngology / Professor and Vice Chair of Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Arkansas Children’s Hospital
Gresham Richter, MD, FACS, FAAP is a Professor, Vice Chair, and Chief of Pediatric Otolaryngology in the Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS) and Arkansas Children’s (AC). Dr. Richter received his undergraduate and medical degrees at the University of Colorado. He completed his residency in Otolaryngology at UAMS and a fellowship in Pediatric Otolaryngology at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital. He returned to Arkansas to join UAMS faculty and founded the Arkansas Vascular Biology Program, a robust laboratory at AC dedicated to understanding and discovering new therapies for complex vascular lesions. Outside of the hospital, Dr. Richter is an entrepreneur and CEO of GDT Innovations.
Professor of Otorhinolaryngology / Director, Pediatric Aerodigestive Center
Baylor College of Medicine / Texas Children's Hospital
Director, Pediatric Aerodigestive Center, Texas Children's Hospital | Professor of Otolaryngology, Baylor College of Medicine. Dr. Mehta's clinical interests are complex airway surgery, pediatric swallowing disorders and head and neck masses,along with general otolaryngology. His research interest includes outcomes of airway surgery, laryngeal cleft management and outcomes of sleep disorders.
2024 Esophageal Phase Dysphagia and Advanced Techniques of Dilation
webinar
Join us for a comprehensive webinar on esophageal phase dysphagia, as part of Bryan Medical’s series on swallowing disorders.
Led by specialists, Dr. Peter Belafsky and Dr. Gresham Richter, this session will explore the latest diagnostic and treatment methods, providing practical skills to enhance your clinical expertise in this challenging medical field.
If you missed our previous webinar in August 2023, you can catch up HERE
Agenda
• Understanding Esophageal Phase Dysphagia
• Exploring Advanced Dilation Techniques
• Q&A Session with Our Expert Panel
Key Topics
• Esophagoscopy
• High-resolution manometry
• EndoFLIP
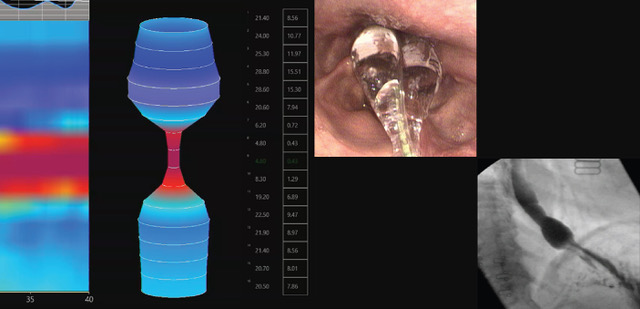
Instructional Video Bonus
You will receive a comprehensive instructional video covering esophageal dilation techniques. The material will serve as a valuable resource to complement the insights you gain from our webinar.
Speaker
Peter Belafsky, MD, MPH, PhD
Dr. Belafsky has dedicated his career to the care of individuals with devastating swallowing disorders. After obtaining a combined Medical Degree and Masters in Public Health from Tulane University in New Orleans, Dr. Belafsky completed a surgical internship and subsequent Ph.D. in Epidemiology from the Tulane University Department of General Surgery and Graduate School. He is currently an Associate Professor at the University of California, Davis.
Moderator
Gresham Richter, MD
Dr. Richter is Professor and Vice Chair of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. He is also currently the President of the American Broncho-Esophagological Association.
news (5)
Csurgeries Was Live! You’ve Matched! What’s Next? With Dr. Juliana Bonilla-velez
news
On April 11th, 2018 we were honoured to have Dr. Juliana Bonilla-Velez host a Facebook Live event titled ‘You’ve Matched! What’s Next?’. Dr. Bonilla-Velez is the chief resident for Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. Originally from Colombia, she is also a founder, editorial board member and former Editor in Chief of the International Journal of Medical Students.
Dr. Bonilla-Velez shared her tips on the exciting transition from medical school to residency. Medical students will find her discussion and step by step instructions interesting and informative as she fills in the gaps in terms of what happens next!
Topics Dr. Bonilla-Velez covers include:
- First off, celebrate, you did it!
- What to do in the months leading up to your residency
- Preparing for paperwork from your new institutions
- Moving to new cities
- Your first day of residency
- Reaching out for support, it’s okay to ask for help
- Educate yourself with survival guide like materials to know what is expected of you
- Managing clinical responsibilities
- Taking care of yourself
- Staying engaged with activities outside the clinic: Volunteering, research, academics, field organisations & associations
- Staying on top of your readings and research to continue progressing in your clinical studies
- Building leadership by getting involved in the medical community, student leadership groups, mentorships
- Setting goals over your residency
- The benefits of working with Journal Publications – IJMS.
Key Take-Aways:
- Your colleagues have all been through it before, they can support you!
- Take your time, don’t get overwhelmed by your clinical responsibilities and make sure to take care of yourself first
- Keep and build connections in academia, the medical community and in your clinical field
- Seek leadership opportunities within your clinical field
- Set goals you can achieve over your residency.
CSurgeries: An International Perspective With Dr. Juliana Bonilla-Velez
news
Dr. Juliana Bonilla-Velez
PGY 4 – Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Tell me a little bit about yourself.
My name is Juliana Bonilla-Velez, and I’m a 4th year resident at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. I’m originally from Colombia, and that’s where I did my medical training. I was very fortunate to work with Dr. Rocco at Mass Eye & Ear Institute as a postdoctoral research fellow on oropharyngeal cancer, and then I came to do my residency training at UAMS. Here, I was also very fortunate to be able to work with Dr. Richter – who is not only one of the founders but an avid promoter of CSurgeries.
He introduced me to CSurgeries very early on in my training. It really is an amazing tool, especially for residents to be able to easily visualize all the things that you are reading! At times, it can be difficult to put all the aspects of a surgery together (especially if you haven’t seen that type of surgery before) or to learn how different people [surgeons] do things. There are so many different techniques for each type of surgery, so I feel like it’s a great avenue that enriches resident education.
Dr. Bonilla-Velez, I understand you published with CSurgeries in June 2016. What can you tell me about your experience? Was it easy? Difficult?
It was my first experience making a video, so that was a little challenging. I was working together with a medical student and we made a really good team. She worked a bit more on the media aspect of helping to put the video together, but then we were able to work together and incorporate some of the more technical aspects of the surgery, and important steps and findings to highlight.
In fact, the recording of the procedure was not difficult at all. It did not interfere with the clinical aspect of what we were doing. The surgery went great, and recording did not obstruct it, make it slower or impose any impediment to the completion of the surgery. At the same time, it was very insightful to be able to review all of it and to put it together in a format that would be easy to teach others what was going on. Not only was it a great experience…it was fun!
It’s very interesting that as a resident you were able to partner with a medical student to take over the technical aspect of video recording and editing while you were able to oversee and supervise the surgical content. Having recently partnered with the International Association of Student Surgical Societies, it confirms that we’re going in the right direction.
Absolutely. Even as a medical student, I was very involved in research and publication. I was actually one of the founders of the International Journal of Medical Students which was an amazing experience, but also gave me a better understanding of the other side of making science. From a medical student’s perspective, it is such an enriching and fulfilling experience to be able to participate in all of these avenues for publishing – participate in research projects, writing manuscripts or making videos – just learning how to think in that way, getting your feet wet and learning all of these skills are so important for the rest of your career as a physician, especially now with evidence-based medicine.
How has publishing with CSurgeries contributed to education as a surgical resident?
As an author, it was very interesting to be able to go through the process of putting the video together, thinking through all the technical aspects of what we were doing and summarizing it in a short format that would be easy to show others.
As a viewer and user of CSurgeries, it allows you to be able to see different techniques for different types of surgeries. Perhaps the Attending at your institution is doing the procedure one way, but seeing how others are doing it in other places certainly enriches your education. In preparation for surgery, CSurgeries publications allow you to see what the steps are, so you can get a more visual understanding of what it is you are going to be doing and what you’re reading in the books. In surgery, even more so than other specialties, this is critical. Learning in 2D in one thing. Being able to see in 3D what it is you’re actually going to be seeing in surgery is quite another. For that reason, CSurgeries is definitely a very valuable tool – especially for people in training.
As a user of CSurgeries, is there a particular CSurgeries publication you recommend (either within or outside of your specialty) you recommend for our members to view and why?
As a 4th year resident, at least in my program, we haven’t started our otology rotation, so I feel like I struggle a little bit more trying to imagine and put together all the otologic surgeries. I haven’t been exposed to them nor have I seen them before. For that reason, one video that was very useful to me that I really enjoyed was Right Stapedotomy that was published by Dr. Babu at the Michigan Ear Institute. Just seeing the video, especially with the ear (it’s such intricate anatomy) was extremely useful. Having access to such a high-quality video that walks you through the surgery, seeing all the steps clearly, was really great.
Of course, there are going to be personal circumstances for which you would find a video more educational than others- depending on what your institution does or your prior experiences. One of the really neat things about CSurgeries is that there’s so much variety- not only within otolaryngology, but among all the other specialties. It’s got something for everyone.
You mentioned you are also a founder of the International Journal of Medical Students. What can you tell me about the IJMS?
Our vision was to create a space that would be made by medical students for medical students to promote research and to provide an avenue for publication that would include all specialties. We aim to speak to medical students who are in a unique part of their training. Not only do we offer a window for them to show their publications, but we are able to help get them to that high-quality level of having a paper that is amenable for publication.
It was also a very exciting to build a team of people that would be able to represent all – not only from around the globe but also those in different stages of their training. We have mentors who have guided us from the beginning, taught us to put all these pieces together and to provide not only an avenue but a service for medical students worldwide where they can publish their work and learn. Especially nowadays where medicine is guided by the paradigm of Evidence-Based Medicine, it’s critical for physicians to be able not only to do research but to understand the research that is published. It serves to train both the authors and the students who are learning to be the editors about all the different aspects of the publication process. It’s been a really very rewarding experience knowing we’ve been able to contribute to medical students’ education worldwide.
How is publishing with CSurgeries different from publishing with IJMS? How are they similar?
It’s different in the sense that the CSurgeries is a video peer-reviewed journal. It’s very visually perfect for the surgical field because it takes you through the novel of each surgery by showing what the key structures are and the key steps you need to be doing. It’s very educational, especially for people in training. In terms of similarities, both aim to educate physicians, students and other surgeons. IJMS provides an avenue for written publication of research along with the more traditional strategies while CSurgeries provides an avenue for video publication. Both share a common mission of education.
What advice do you have for international medical graduates looking to pursue surgical residency in the United States?
It’s certainly a very difficult task, but at the same time, it can be immensely rewarding. You have to be very passionate about what you want to do, what you want to accomplish, and what you want for your life. If your goals are clear and you can translate all that passion into hard work and dedication to your specialty, that goes a long way. It’s certainly hard but not impossible. I’d highly encourage you to push through the difficulties if you feel that’s your life mission. Don’t give up on your dreams.
What would you be doing if you were not a surgeon?
Oh gosh! There is nothing else I would rather be doing! I wish I could have a parallel life to be able to do all the things I want to do, but all at the same time. But certainly the life I would not give up is being a future pediatric otolaryngologist and be able to continue to participate in academics, in research and education, and in clinical practice and leadership. I look forward to playing a part in furthering the field
Watch Dr. Juliana Bonilla-Velez’s video Excision of Thyroglossal Duct Cyst and her Facebook Live, You’ve Matched, What’s Next?
Michael Golinko Was Live! Craniosynostosis: A Surgeon's Perspective
news
On February 14th, 2018 we were honored to have Michael S. Golinko MD, MA, FAAP, host our first Facebook Live. Dr. Golinko is one of our valued CSurgeries Section Editors for Plastic Surgery, Medical Director of the Craniofacial Anomalies Program at the Arkansas Children’s Hospital, and an Assistant Professor of Plastic Surgery for the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences.
Dr. Golinko was a great presenter during the live event and shared his views on best practices for approaching craniosynostosis. His discussion on the subject provides information that both surgeons, medical students, and patients will find interesting and informative.
Topics Dr. Golinko covers include:
- What is craniosynostosis
- How common is craniosynostosis
- Types of craniosynostosis – sagittal, coronal, metopic, lambdoid
- Craniosynostosis vs. plagiocephaly
- Brain growth in the first year of life
- Facts about the development of the brain and development issues that might occur with craniosynostosis
- The importance of operating on the skull when an infant has craniosynostosis to allow for normal brain growth
- Common consults including flat head, closed soft spot, suture closure, and premature fusion
- Signs, symptoms, and risks of craniosynostosis
- Downstream effects of untreated craniosynostosis
- Treatment options for addressing craniosynostosis – cranial vault remodeling, spring assisted
- Survivor rates and complications
Watch the recorded Facebook Live here!

Dr. Golinko also walks us through his team’s published CSurgeries video Fronto-Orbital Advancement and Cranial Vault Remodeling for Metopic Craniosynostosis. He discusses why he recommends CSurgeries as an educational tool for both surgeons and medical students and wraps up by answering questions on the topic.
Dr. Golinko shared his presentation here.
A special thanks to Dr. Michael Golinko for hosting such an informative Facebook Live.
Introducing our presenters for the upcoming Cleft Lip Revision webinar!
news
This webinar comes as the latest in a long line of installments dealing with the Cleft Palate. In this session, attendees will learn various tips and tricks to a successful cleft lip revision procedure. There will be a Q&A session to discuss common challenges and how to address them.
Meet the Course Directors


Director of Cleft Lip and Palate / Pediatric ENT Surgeon
Arkansas Children's Hospital / University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Larry Hartzell, MD FAAP is an Associate Professor of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery at Arkansas Children’s Hospital. He is the Director of the Pediatric Otolaryngology fellowship. Dr Hartzell also has been the Cleft Team Director in Arkansas since 2012. He is passionate about international humanitarian mission work and dedicates much of his research efforts to cleft surgical and clinical care as well as velopharyngeal insufficiency. Dr Hartzell is actively involved in multiple academic societies and organizations including the AAO-HNS and ACPA.
Professor / Director of Division of Otolaryngology
Emory University School of Medicine / Children's Healthcare in Atlanta
Dr. Goudy is a professor at Emory University School of Medicine and the director of the division of otolaryngology at Children’s Healthcare in Atlanta. Dr. Goudy’s clinical job involves repair of craniofacial malformations including cleft lip, cleft palate, and Pierre Robin sequence, and he also participates in head and neck tumor resection and reconstruction.
Meet the Presenters


Associate Professor of Department of Otolaryngology--Head & Neck Surgery, Division of Pediatric Otolaryngology
University of North Carolina - Chapel Hill
Dr. Leeper completed her residency training in Otolaryngology--Head & Neck Surgery at the Medical University of South Carolina in 2012 and fellowship training in Pediatric Otolaryngology at Arkansas Children's Hospital in 2014. She returned to the University of North Carolina - Chapel Hill in 2014 on faculty in the Department of Otolaryngology--Head & Neck Surgery. She is the current Fellowship Director and Medical Director of the Children's Cochlear Implant Center. She is married to Bradley and they have one daughter Sutton and a baby boy arriving this month.
Residency Program Director / Director Cleft and Craniofacial Team
Carle Foundation Hospital
Dr. Manlove joined Carle Foundation Hospital in 2016 as a fellowship trained cleft and craniomaxillofacial surgeon. She is the director of the cleft and craniofacial team at Carle. In 2018 she was name “Rising Star Physician” and that same year she also became the residency program director. Outside of work, she loves spending time with her family and she is an avid runner.


Associate Professor - Craniofacial Abnormalities & Pediatric Otolaryngology / Co-Director of Cleft and Craniofacial Team
University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics
Dr. Kacmarynski is a Clinical Associate Professor in the Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery at the University of Iowa, working as a pediatric otolaryngologist and a cleft and craniofacial surgeon with co-directorship for the cleft and craniofacial team at the University of Iowa. Research focus is on biomedical collaborations with oral cleft and craniofacial surgical problems including craniofacial airway, tissue engineering solution development, outcomes research and patient-centered outcomes research collaboratives. I am excited about the long-term impacts of research leading very directly to significant improvements in o
Linton Whitaker Endowed Chair in Craniofacial Surgery
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Division of Plastic Surgery
Jordan Swanson, MD, MSc, is an attending surgeon in the Division of Plastic, Reconstructive and Oral Surgery at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia with special clinical expertise in cleft, craniofacial, and pediatric plastic surgery. He holds the Linton A. Whitaker Endowed Chair in Plastic, Reconstructive and Oral Surgery.
Author Spotlight: A Conversation with Soroush Farsi
news
Soroush Farsi is a fourth-year medical student at Texas Tech University and an ENT clinical research fellow at the University of Arkansas for Medical Science for his gap year. His experiences in Turkey, working as a translator in hospitals and seeing how remarkable the role that doctors play, fueled his passion for medicine. Specializing in otolaryngology-head and neck surgery, Soroush has carved a niche for himself not just as a dedicated medical professional but as a content creator shaping the future of surgical education.
After arriving in the U.S., Soroush worked various jobs that enabled him to work his way through his education at Texas A&M University. In 2019, he earned a degree in nutritional science with a minor in biology and graduated with a Summa Cum Laude distinction.
Soroush's journey as a content creator began five months ago with a chance introduction to CSurgeries.com by none other than Dr. Gresham Richter, the Executive Chairman of the platform.
“I was motivated to become a content creator after learning extensively from the platform. Inspired by the commitment to sharing valuable surgical insights, I contribute by uploading videos of interesting procedures encountered during my shadowing experiences.”
For Soroush, creating surgical content is a meticulous and collaborative process.
“My process for creating surgical content typically begins with reaching out to various surgeons at our ENT department, inquiring about compelling cases suitable for videotaping. After ensuring there isn't a similar video in the database, I coordinate with the surgeon and obtain patient consent before recording the procedure. Following the editing and review by the surgeon, I craft a procedural abstract and upload the content to CSurgeries.com. This workflow ensures the dissemination of valuable and unique surgical insights on the platform.”
Soroush acknowledges the challenge of condensing extensive surgeries into concise, educational videos.
“To overcome this hurdle, extensive reading and research about the procedures have been invaluable in identifying the crucial and significant aspects to include in the video. Dr. Richter's guidance has been particularly helpful; he emphasized the importance of envisioning the video as a tutorial for medical students, aiming to enable them to perform the procedure after watching. This perspective has been instrumental in ensuring the videos are not only informative but also effective in educating and empowering viewers.”
Soroush recounts a poignant instance where his content had a profound impact on a seasoned surgeon nearing retirement.
“A seasoned surgeon I closely collaborate with is nearing retirement after over 60 years of experience in head and neck surgery. He expressed profound interest in recording his unique surgical approaches and procedures, not commonly performed by ENTs. Our discussions revolve around identifying potential new cases to be taped and uploaded, ensuring that his wealth of knowledge continues to benefit others even after his retirement. It's immensely rewarding to contribute to the preservation and sharing of such valuable insights within the medical community.”
According to Soroush, aspiring content creators must embrace collaboration with surgeons in the editing process.
“For those aspiring to become content creators in surgical education, my advice is to actively involve the surgeon in the editing process to guarantee the production of high-quality and educational videos. This collaborative approach not only enhances the educational value but also ensures that the material is presented in a manner conducive to effective learning.”:
Reflecting on his journey, Soroush highlights the transformative impact of being a content creator for CSurgeries on his personal growth and professional development.
“The process of watching, editing, reviewing, and researching each video I publish has transformed me into an expert in those procedures. This heightened expertise not only boosts my confidence in identifying landmarks but also strengthens my ability to recall procedural steps. As I envision my future as a resident surgeon, this experience has significantly contributed to my readiness and proficiency in the surgical domain.”
As Soroush peers into the future of surgical education, he envisions a shift away from conventional learning methods towards dynamic, visual experiences.
“I anticipate a transformation in the landscape of surgical education, moving away from conventional methods of learning procedural steps through books. Sometimes, a 5-minute video can deliver more knowledge than hours of reading. This not only streamlines the learning process but also fosters confidence and improves retention. Personally, my commitment to this evolution involves creating and sharing educational videos that offer a dynamic and great learning experience.”
Soroush stands as a testament to the power of collaborative, visually-driven surgical education, leaving an indelible mark on the future of medical learning. Through his work, he not only imparts knowledge but also cultivates a community committed to the continuous evolution of surgical education.